Java is renowned for its “write once, run anywhere” capability, making it one of the most versatile programming languages. Let’s explore the key features and mechanisms that make Java platform independent.
Why Java is Platform Independent?
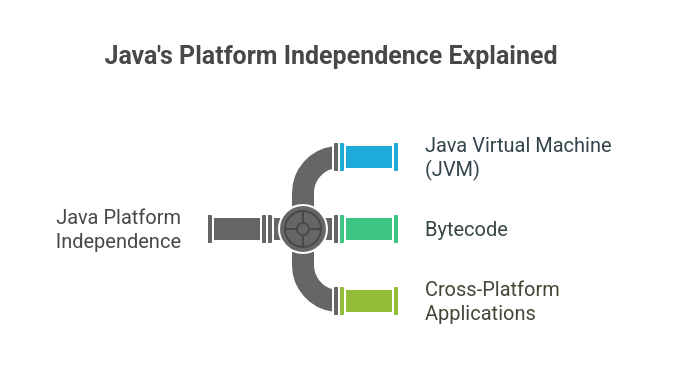
Java is “platform-independent” because the code written in Java can run on any operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux, etc.) without requiring any changes. This is due to its “Write Once, Run Anywhere” (WORA) feature, which is made possible by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
The Role of Bytecode
When you write and compile a Java program, the code is converted into a special intermediate form known as bytecode.
Unlike machine code, which is specific to a particular operating system or hardware, bytecode is a universal format that can be executed on any platform.
The Role of the JVM
The JVM is a key component that makes Java platform-independent. It acts as an interpreter that translates the platform-neutral bytecode into machine-specific instructions that the operating system and hardware can understand.
Each operating system has its own version of the JVM:
- Windows has a Windows JVM.
- Linux has a Linux JVM.
- macOS has a macOS JVM.
Despite these differences, all JVMs can execute the same bytecode, ensuring compatibility across platforms.
Abstract Machine Concept
The JVM acts like a virtual machine that runs the program. It hides the details of the operating system and hardware and make sure that the code works the same way on any platform. This abstraction ensures that the code remains portable.
Cross-Platform Libraries
Java libraries, such as java.io for input/output, java.net for networking, and java.sql for database operations, are built to behave consistently across platforms. As a result, no changes are needed to the code to make it compatible with different operating systems.
How Java Programs Work
- Writing the Code: You write a Java program in a .java file.
- Compilation: The Java compiler (javac) processes the code and generates bytecode stored in a .class file.
- Execution: The JVM reads this bytecode, converts it into platform-specific machine code, and runs the program.
For example, consider this Java program:
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}
When we compile this program, it generates a .class file containing bytecode. This bytecode can run on Windows, Linux, or macOS without any changes, as long as a compatible JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is available on the system.
Understand the methods in Java and how they help organize and structure your code effectively.
Conclusion
Java is platform independent because of its use of bytecode and the JVM. While the bytecode is universal and platform-neutral, the JVM is platform-dependent. Each operating system has its own JVM, which ensures that the same bytecode can be executed seamlessly across different platforms.
Quiz
Q1. Which component makes Java platform-independent?
Q2. What does the Java compiler (`javac`) do?
Q3. Why is Java bytecode considered platform-independent?
Q4. What does “Write Once, Run Anywhere” (WORA) mean in Java?
Related Topics: