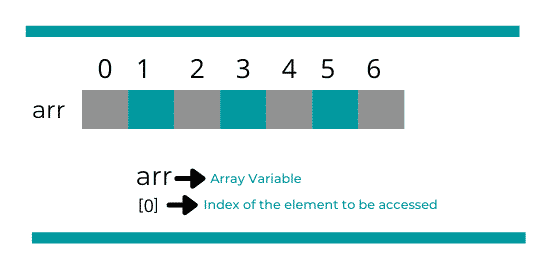
What is an Array?
An array is a collection of similar data elements stored at contiguous memory locations. It is the simplest data structure where each data element can be accessed directly by only using its index number.
For example, if we want to store the marks scored by a student in 5 subjects, then there’s no need to define individual variables for each subject. Rather, we can define an array that will store the data elements at contiguous memory locations.
Array marks[5] define the marks scored by a student in 5 different subjects where each subject’s marks are located at a particular location in the array, i.e., marks[0] denote the marks scored in the first subject, marks[1] denotes the marks scored in 2nd subject and so on.
Different Types Of Arrays
- Single-Dimensional Arrays (1-D)
- Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- Three-Dimensional (3-D) Arrays
- Dynamic Arrays
- Character Arrays
To learn how different arrays in C work, check out our blog “Types of Array in C.“
What Is The Need of using Array?
In programming, most of the cases need to store a large amount of data of a similar type. We need to define numerous variables to store such a huge amount of data.
While writing the programs, it would be very tough to memorize all variable names. Instead, it is better to define an array and store all the elements in it.
The following example illustrates how an array can be used while writing a code-
In the following example, we have given marks to a student in 5 different subjects. The aim is to calculate the average of a student’s marks.
Using Array
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int subject1 = 40, subject2 = 52, subject3 = 47, subject4 = 70, subject5= 67;
float avg = (subject1 + subject2 + subject3 + subject4 + subject5)/5;
printf(avg);
}
Without Using Array
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int subject1 = 40, subject2 = 52, subject3 = 47, subject4 = 70, subject5= 67;
float avg = (subject1 + subject2 + subject3 + subject4 + subject5)/5;
printf(avg);
}
What Are The Types Of Indexing In Array?
· 0 (Zero Based Indexing)- The first element of the array refers to index 0.
· 1 (One Based Indexing)- The first element of the array refers to index 1.
· n (n Based Indexing)- The base index of an array can be chosen as per requirement.
What Is The Complexity of Array Operations?
Time Complexity
| Algorithm | Average case | Worst case |
| Access | O(1) | O(1) |
| Search | O(n) | O(n) |
| Insertion | O(n) | O(n) |
| Deletion | O(n) | O(n) |
The space complexity of an array for the worst case is O(n).
What Are The Advantages of Array?
- Arrays represent multiple data elements of the same type using a single name.
- Accessing or searching an element in an array is easy by using the index number.
- An array can be traversed easily just by incrementing the index by 1.
- Arrays allocate memory in contiguous memory locations for all its data elements.
How To Access Elements in an Array?
To access any element of an array, we need the following details:
- Base Address of array.
- Size of an element in bytes.
- Which type of indexing array follows.
The address of any element of a 1D array can be calculated by using the below-given formula:
Byte address of an element A[i] = base address + size * (i – first index)
How To Pass Array To a Function?
As mentioned earlier, the name of an array represents the address of the first element of the array. The elements of an array can be traversed just by using the base address.
The below example illustrates how an array can be passed to a function.
The below program defines a function named total, which accepts an array as an argument. This function calculates the sum of all the elements of the array.
#include<stdio.h>
int total(int[]);
void main()
{
int arr[5] = {0,1,2,3,4};
int sum = total(arr);
printf(“%d”,sum);
}
int total(int arr[])
{
int sum=0;
int i;
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
{
sum = sum + arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
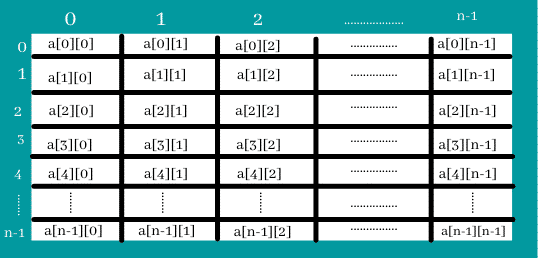
What is 2D Array?
2 Dimensional arrays are often defined as an array of arrays. A 2D array is also called a matrix. A matrix can be depicted as a table of rows and columns.
Also, now you can learn Arrays in C Programming in Hindi
How To Declare 2D Array?
The syntax of declaring a 2D array is very much similar to that of an 1D array.
Syntax –
int arr[max_rows][max_columns];
It produces data structure as shown below:
How to access data in a 2D array?
As in a one-dimensional array, data can be accessed by using only an index, and similarly, in a two-dimensional array, we can access the cells individually by using the indices of the cells. There are two indices attached to a single cell, one is its row number, and the other one is its column number.
Syntax to store the value stored in any particular cell of an array –
int x = a[i][j];
Here i and j are the row and column indices, respectively.
Initializing 2D array –
When we declare a one-dimensional array, there’s no need to specify the size of the array, but it’s not the same for a two-dimensional array. For a 2D array, we need to specify at least the row size, i.e., the second dimension.
Syntax to declare 2D array –
int arr[2][2] = {1,2,3,4}
The number of elements present in a 2D array will always be equal to (number of rows * number of columns).
Example :
C program to store user’s data into a 2D array
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int arr[4][4],i,j;
for (i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for (j=0; j<4; j++)
{
printf(“Enter value for arr[%d][%d]: “ i,j);
scanf(“%d”,&arr[i][j]);
}
}
}
Java program to store user’s data into a 2D array
import java.util.Scanner;
publicclass ArrayTwoD {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = newint[4][4];
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<4;j++)
{
System.out.print(“Enter Data”);
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
Mapping 2D to 1D array –
2D arrays are mainly created to implement a database table that look alike data structure. Whilst in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D arrays is similar to that of one-dimensional arrays.
The size of a 2D array is always equivalent to the product of the number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. Thus, we need to map two-dimensional arrays to one-dimensional arrays so as to store them in the memory.
A 3 X 3 2D array is shown in the image below.
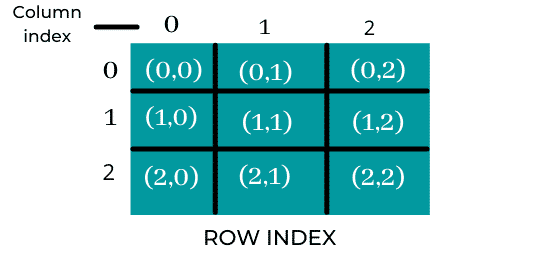
There are 2 main techniques to map a two-dimensional array to one-dimensional array.
- Row Major Ordering
In row-major ordering, all the rows of the two-dimensional array are stored in a contiguous manner in the memory. Considering the array shown within the above image, its memory allocation according to the row-major order technique is shown below.
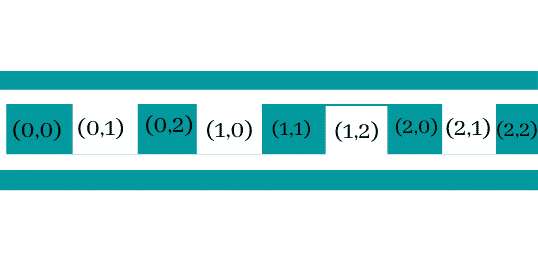
First, we insert elements of the 1st row of the 2D array into the memory, followed by the elements of the 2nd row and so on.
- Column Major Ordering
In column-major ordering, all the columns of the two-dimensional array are stored in a contiguous manner in the memory. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation consistent with the column-major order technique is shown below.
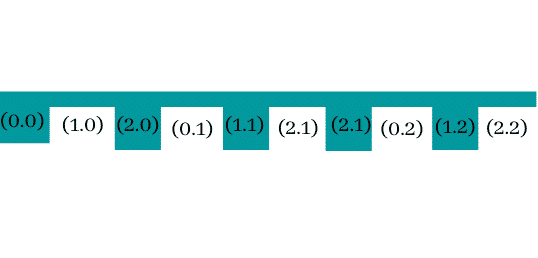
First, we insert elements of the 1st column of the 2D array into the memory, followed by the elements of the 2nd column, and so on.
Conclusion
Learn everything about arrays and broaden your knowledge with a Postgraduate Program in Software Development designed by industry experts. This program covers everything from programming basics to databases and includes multiple coding challenges. It prepares you for top tech and product companies. Advance your skills with the PG Program in Software Development.
FAQs
An array is a data structure used to store multiple elements of the same type under a single variable name. It organizes data so that a related set of values can be easily sorted or searched.
You can access elements in an array by referring to the index number associated with each element. The index of the first element is 0, the second element is 1, and so on.
Typically, arrays are meant to store elements of the same type. However, in languages like JavaScript, arrays can store elements of different types because they are implemented as objects.
Multidimensional arrays are arrays that contain other arrays as their elements. These are used to represent more complex structures like matrices.
Arrays allow fast access to elements as you can directly jump to any element using its index. This makes reading data very efficient. They also simplify the management of large datasets by allowing operations on multiple items at once.
Modifying arrays can be inefficient, especially if you need to add or remove elements in the middle of the array because this requires shifting elements to maintain order. Also, in some programming languages, arrays have a fixed size once they are created, which limits their flexibility.
In Java, you can initialize an array either by specifying the size and then filling it, or by directly filling it with elements at the time of declaration. For example, int[] myArray = new int[10]; initializes an array with space for 10 integers, whereas int[] myArray = {1, 2, 3}; initializes and fills the array at the same time.