- Introduction
- What are lean principles?
- 5 Lean Principles everyone should know
- Things to do before applying lean principles
- Applying the Principles
- Conclusion
Introduction
In today’s business world, the term “lean” is used a lot. You may have heard it used in relation to manufacturing, software development, or even in relation to business process management in general. But what does lean mean, and what are lean principles and why is it so important?
In a nutshell, lean principles are all about maximising value and minimising waste. That may sound simple, but it’s actually quite difficult to achieve in practice. That’s because many types of waste can creep into any type of process, whether manufacturing, software development, or something else entirely.
The good news is that many lean principles and tools can help you identify and eliminate waste in your own processes. By applying lean principles, you can make your processes more efficient and effective and ultimately improve your bottom line.
What are Lean Principles?
The lean principles are a set of guidelines that can be used to improve any process. They are based on the philosophy of lean manufacturing, which is a system that aims to waste as little as possible and produce only what is needed. The lean principles can be applied to any type of organisation, not just manufacturing.
There are a number of reasons why lean principles are important. First, lean helps organisations to identify and eliminate waste. This is important because it helps to improve efficiency and productivity. Second, lean helps to improve quality by reducing defects and rework. This is important because it helps to improve customer satisfaction and reduce costs. Third, lean helps to improve safety by reducing accidents and injuries. This is important because it helps to protect employees and improve the organisation’s bottom line. Finally, lean helps to improve morale by increasing employee engagement and satisfaction. This is important because it helps to improve retention and attract new talent.
5 Lean Principles everyone should know
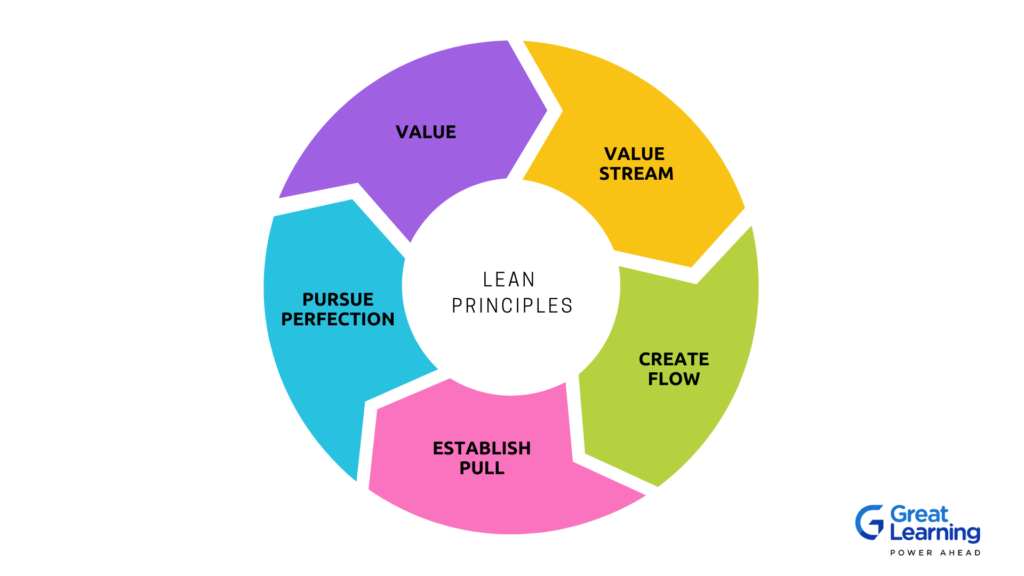
- Value: In lean principles, value is defined as anything that provides benefit to the customer. This includes anything from the product or service itself to the packaging and delivery. The value in lean principles is the ability to create value for the customer while minimising waste. This is done by identifying the value stream and then eliminating waste throughout the process.
- Value Stream: A value stream is a series of activities that create value for the customer. In a lean organisation, value streams are the primary means of getting work done and creating value. The “value stream” comes from the Toyota Production System, which describes the end-to-end process for creating products and delivering them to customers. In the TPS, every value stream is comprised of three activities:
- Value-creating activities – These are the activities that actually create value for the customer. Examples include design, manufacturing, and assembly.
- Value-enabling activities – These are the activities that support value-creating activities. Examples include procurement, logistics, and quality control.
- Value-destroying activities – These are the activities that do not create value for the customer but are necessary for the product or service to be delivered. Examples include waste, rework, and scrap.
The goal of lean is to identify and eliminate value-destroying activities and to minimise value-enabling activities. This creates a lean value stream, which is able to produce more value for the customer with less effort.
- Create Flow: The create flow principle is one of the core lean principles. It is based on the idea that the best way to create value for the customer is to have a smooth, uninterrupted flow of work. This principle is often called “the principle of continuous flow.” Creating flow in lean principles means creating a smooth and uninterrupted flow of work from one process to the next. This can be achieved by eliminating waste and unnecessary steps in the process and by ensuring that each process is properly linked to the next.
- Establish Pull: The basic idea behind pull is that work only starts when there is a demand for it. This demand can come from downstream processes in the value stream or from the customer. The purpose of pull is to avoid having too much inventory in the system, which can lead to waste.
The establish pull principle in lean thinking is based on the idea that each step in a process should only produce what is needed by the next step in the process when it is needed. This principle is intended to help reduce waste and increase efficiency by ensuring that there is no inventory build-up between steps in a process.
- Pursue Perfection: The pursuit of perfection is a core principle of lean thinking. The idea is always to look for ways to improve the quality of your products or services and never to be satisfied with mediocrity. This principle is often referred to as “kaizen,” which is the Japanese word for “improvement.” Pursuing perfection in lean principles means striving to eliminate waste in all forms in order to create value for the customer. This can be achieved by constantly improving processes and systems and involving all employees in the continual improvement process.
Things to do before applying lean principles
However, some general recommendations include:
1. Conduct a thorough analysis of the organisation’s current state to identify areas of waste and potential improvement.
2. Develop a clear understanding of lean principles and how they can be applied to the specific organisation.
3. Create a detailed plan for implementing lean principles, including specific goals and objectives.
4. Obtain buy-in and support from senior management and other key stakeholders.
5. Train all employees on the basics of lean thinking and principles.
6. Implement lean principles gradually, starting with small pilots in specific areas.
7. Monitor and measure progress regularly, making adjustments as necessary.
Applying the Principles
There are a few key ways to apply lean principles:
1. Eliminate waste: One of the main goals of lean is to eliminate waste in all forms. This means looking at every process and identifying ways to eliminate steps that don’t add value.
2. Streamline processes: Another key goal of lean is to streamline processes so that they are as efficient as possible. This means identifying ways to eliminate bottlenecks and reduce cycle times.
3. Improve communication: Another key element of lean is effective communication. This means ensuring that everyone involved in a process is on the same page and knows what needs to be done.
4. Empower employees: Lean also emphasises empowering employees so that they can take ownership of their work and be more effective. This means giving employees the authority to make decisions and ensuring that they have the resources they need to be successful.
Conclusion:
Implementing lean principles can profoundly and positively impact any organisation, large or small. Lean principles can help eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction when done correctly.
They are a great way to improve your productivity and efficiency. By following these principles, you can streamline your work process and get more done in less time.