Did you know?
AI agents are the driving force behind many of the smart technologies we use daily, from virtual assistants like Siri to recommendation systems on Netflix.
But what exactly are AI agents, and how do they work?
In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll explore the concept of AI agents, their role in creating autonomous systems, and how they’re transforming industries worldwide.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are software programs that use artificial intelligence (AI) to perform tasks for a user or another system. They can interact with their environment, collect data, and use that data to make decisions and take actions.
These agents function autonomously, meaning they don’t require constant human intervention, and many can improve their performance through learning.
They are widely used in various applications, from virtual assistants to self-driving cars. For example, Alexa, Siri, Google Assistant, etc.
Also Read: What is Generative AI?
Core Components of AI Agents
1. Perception:
AI agents collect & interpret data from their environment using multiple inputs such as:
- Sensors
- Cameras
- Microphones
- Software APIs
This enables them to understand what’s happening around them.
Example: A chatbot processes customer input through text analysis or voice recognition.
2. Decision-Making:
Once the data is collected, the agent uses algorithms, predefined rules, or machine learning models to analyze the information and make decisions. These decisions aim to achieve specific objectives or solve problems.
Example: The chatbot determines the best response to a customer query based on its training data or programmed logic.
3. Action Execution:
After decision-making, the agent operates an action to fulfil its purpose. This could vary from generating text responses to controlling a robotic arm in a factory.
Example: The chatbot delivers a text-based reply or speaks the answer to the customer’s query.
Types of AI Agents
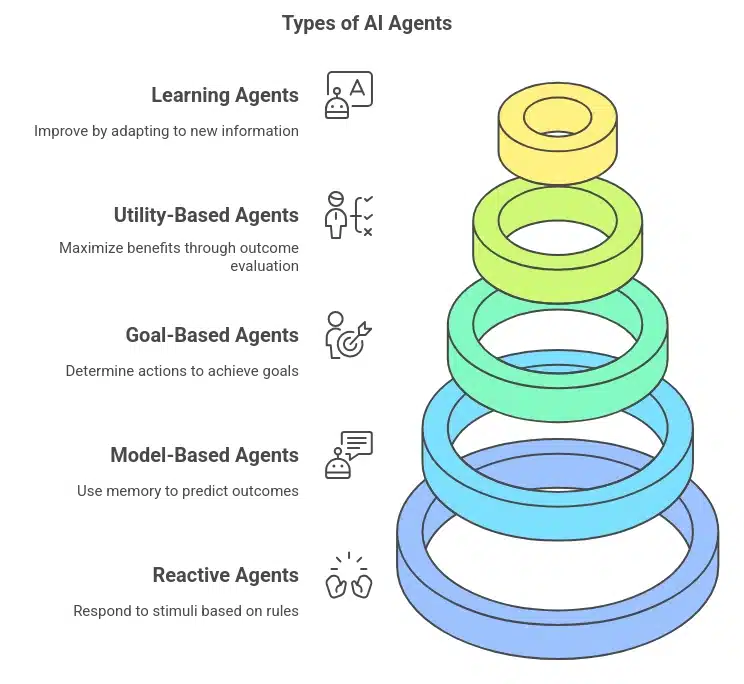
There are five types of AI Agents:
1. Reactive Agents
These agents have no memory and cannot learn or adapt. They respond directly to stimuli in their environment based on predefined rules or patterns.
Example: Chess-playing programs like Deep Blue make decisions solely based on the active state of the game without taking past moves into account.
2. Model-Based Agents
These agents use memory & a model of the world to understand their environment & predict the outcomes of their actions.
Example: GPS navigation systems that consider active location, traffic situations, & destination to suggest optimal routes.
3. Goal-Based Agents
These agents operate by considering predefined goals & determining the actions required to achieve them.
Example: Self-driving cars plan routes and make driving decisions based on the goal of reaching a destination safely & efficiently.
4. Utility-Based Agents
These agents evaluate possible outcomes of their actions & choose the one that maximizes overall utility or benefits.
Example: E-commerce recommendation systems suggest products to users based on their preferences & the likelihood of purchase, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction & sales.
5. Learning Agents
Definition: These agents improve their performance over time by learning from data and adapting to new information. They can refine their decision-making processes based on past experiences.
Example: Virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa learn user preferences and improve their ability to answer questions, set reminders, or control smart devices.
How AI Agents Work?

1. Perception:
AI agents collect data from their environment using large number of inputs such as:
- Sensors
- Cameras
- Microphones
This allows them to understand their surroundings & detect changes or stimuli.
2. Processing:
The agent then processes further with processing the collected data through algorithms, machine learning models, or predefined rules.
This step necessitates analyzing the information to recognize patterns, make predictions, or assess actions based on the agent’s goals.
3. Action:
After processing the information, the AI agent takes proper action according to its decision-making procedure.
Action may be sending commands and responses as well as performing a physical activity that aligns with the accomplishment of a predetermined goal.
4. Feedback Loop:
This process entails the monitoring of the results obtained and comparing these results with those that were anticipated.
The feedback adjusts its behaviour or decision-making based on this difference and improves with time.
Continuous improvement in action in pursuit of improved efficiency and accuracy helps the agent to refine the action.
This process allows AI agents to interact dynamically with their environment and improve autonomously.
Also Read: AI Agents vs Agentic AI
Benefits of AI Agents
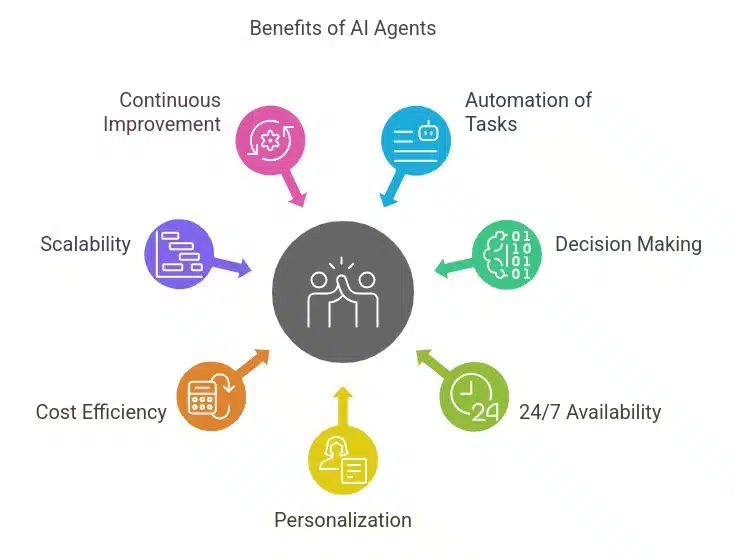
1. Automation of Repetitive Tasks:
The AI agent can do tasks that require repetition. This leaves human employees to concentrate on either complex or creative activities, thus enhancing efficiency and minimizing the occurrence of human error.
2. Better Decision Making
AI agents are quick and accurate in analyzing huge volumes of data. They assist organizations in making more informed decisions. They may notice patterns or trends that the human eye cannot.
3. 24/7 Availability:
Unlike humans, AI agents do not get tired. They can work round-the-clock without getting tired. This makes them ideal for tasks like customer support, where they can provide instant responses and support at any time of day.
4. Personalization
AI agents can learn from user data & preferences, thus providing personalized recommendations, services as well as experiences.
For instance, recommendation engines in e-commerce suggest products based on past behavior.
5. Cost Efficiency:
By automating tasks, AI agents reduce the need for human intervention, which can lower labor costs. They can also streamline processes & increase productivity, which can lead to long-term cost savings.
6. Scalability:
AI agents can easily scale to handle larger volumes of tasks or users. For instance, chatbots can manage thousands of customer queries simultaneously, something that would be impossible for human agents to handle.
7. Continuous Improvement:
Most AI agents, particularly those using machine learning, are always improving performance with time, by learning from new data and experiences, adapting to changing environments, and increasing their effectiveness.
These benefits make AI agents a powerful tool across a variety of industries, enhancing productivity, decision-making, and customer satisfaction.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
1. Healthcare:
Virtual health assistants use AI agents to answer patient questions, schedule appointments, and remind patients to take medication.
AI-based diagnostic tools examine medical images & patient data to identify conditions such as cancer or heart disease, offering faster & more accurate diagnoses.
2. Finance:
In the finance sector, AI agents are employed in fraud detection systems, monitoring transactions for unusual patterns and preventing unauthorized activities.
Additionally, AI-driven automated trading systems can analyze market trends and execute trades at optimal times, making real-time decisions to maximize profits.
3. Transportation:
An example is autonomous vehicles: self-driving cars use AI agents to perceive surroundings, make decisions about driving, and ensure a safe way of driving.
AI is applied in route optimization systems that evaluate traffic, weather, & road conditions to help drivers & logistics companies take the fastest & most efficient paths possible.
4. Customer Service:
AI-powered chatbots and virtual agents are managing customer inquiries while offering 24/7 support.
These virtual agents understand the natural language so they can correctly and promptly reply to customer insatisfactionquiries, thus leading to efficiency and increased user.
These applications demonstrate how AI agents are transforming various industries by automating tasks, enhancing efficiency, and providing personalized experiences.
Future of AI agents
Here are some key trends shaping the future of AI Agents:
- Autonomous Decision-Making: AI agents will become more capable of making decisions independently, enhancing their ability to adapt to dynamic environments and solve problems in real-time.
- Human-AI Collaboration: AI agents will work alongside humans, enhancing productivity and decision-making in industries such as healthcare, finance, and customer service.
- Personalization: AI agents will deliver highly personalized experiences by analyzing individual preferences, behaviors, and needs, improving user engagement and satisfaction.
- Ethical and Transparent AI: With the increasing role of AI, there will be a strong focus on ensuring AI agents operate ethically, transparently, and align with societal values to foster trust and accountability.
- Ubiquity in Daily Life: AI agents will become embedded in daily life, from virtual assistants in smart homes to autonomous vehicles, transforming how we live and interact with technology.
As AI evolves, these agents will push the boundaries of what’s possible, offering unprecedented opportunities and challenges in technology, ethics, and human interaction.
Related Free Courses: