In today’s digital world, data is the backbone of decision-making and technology. However, not all data is the same; it can be broadly classified into structured and unstructured data. While structured data is neatly organized in databases, unstructured data exists in raw formats like text, images, and videos.
Understanding the key differences between these data types is essential for businesses, data scientists, and AI professionals.
In this article, we will be talking about the features, examples, and importance of structured and unstructured data.
What is Structured Data?
Structured data refers to organized and well-formatted data that follows a predefined schema, making it easy to store, retrieve, and analyze. It is usually stored in relational databases and arranged in a tabular format with rows and columns.
Characteristics of Structured Data
- Organized format: Stored in a well-defined structure.
- Fixed schema: Data fields are predefined (e.g., name, age, salary).
- Easily searchable: Can be queried using SQL (Structured Query Language).
- Highly scalable: Can be expanded easily in relational databases.
- Low storage complexity: Requires less space compared to unstructured data.
Examples of Structured Data
- Business and Financial Data: Customer databases, employee records, financial transactions.
- Inventory Management: Product IDs, stock levels, supplier details.
- Web Analytics: Page views, click-through rates, user session durations.
- Machine-Generated Logs: IoT sensor readings, transaction logs, GPS data.
Storage of Structured Data
- Relational Databases (RDBMS): MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle.
- Spreadsheet Software: Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets.
What is Unstructured Data?
Unstructured data refers to data that does not follow a fixed format or predefined schema. It is often stored in raw form and requires specialized processing techniques to extract meaningful information.
Characteristics of Unstructured Data
- No predefined format: Data exists in various formats (text, images, videos, etc.).
- Difficult to store and process: Cannot be easily stored in traditional databases.
- Requires advanced tools: Needs technologies like AI, NLP, and Big Data tools for processing.
- High storage complexity: Requires more space compared to structured data.
- Diverse sources: These can come from multiple channels like emails, social media, and IoT devices.
Examples of Unstructured Data
- Text Data: Emails, social media posts, blogs, customer reviews.
- Multimedia Data: Images, videos, audio recordings.
- Scientific Data: Medical scans, satellite images, genetic data.
- Web and IoT Data: Logs, sensor data, clickstream data.
Storage of Unstructured Data
- NoSQL Databases: MongoDB, Cassandra, Amazon DynamoDB.
- Data Lakes & Cloud Storage: Google Cloud Storage, AWS S3, Hadoop.
Key Differences Between Structured and Unstructured Data
| Feature | Structured Data | Unstructured Data |
| Format | Organized in rows & columns | No predefined format |
| Schema | Fixed and well-defined | No fixed schema |
| Storage | Relational databases (SQL) | NoSQL databases, data lakes |
| Ease of Analysis | Easy with SQL queries | Requires AI, NLP, Big Data tools |
| Examples | Customer records, sales data | Emails, videos, social media posts |
| Processing Tools | SQL, BI tools | Hadoop, NLP, AI models |
| Scalability | High in RDBMS | High in NoSQL & cloud storage |
What is Semi-Structured Data?
Semi-structured data falls between structured and unstructured data. It contains some organization level but does not follow a rigid tabular format.
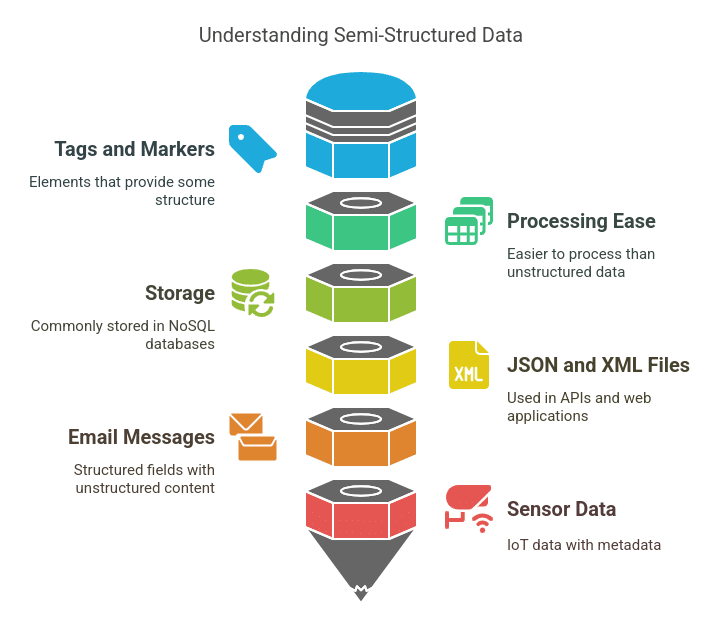
Characteristics of Semi-Structured Data
- Contains tags, markers, or metadata to provide some structure.
- It is not as rigid as structured data but more straightforward to process than unstructured data.
- Commonly stored in NoSQL databases.
Examples of Semi-Structured Data
- JSON and XML Files: Used in APIs and web applications.
- Email Messages contain structured fields (sender, receiver) and unstructured content (email body).
- Sensor Data: IoT-generated readings with metadata.
Check out these free data science courses to learn essential concepts, and hands-on data techniques.
Uses of Structured and Unstructured Data
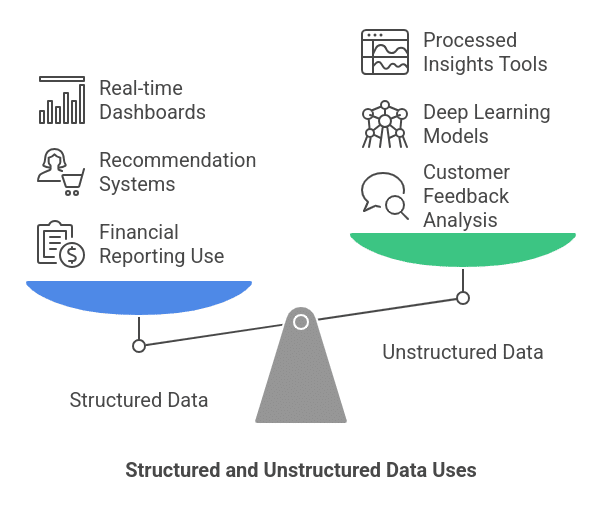
1. Business and Decision Making
- Structured Data is used for financial reporting, customer relationship management (CRM), and business intelligence.
- Unstructured Data helps companies analyze customer feedback, brand sentiment, and market trends.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- AI models rely on both types of data. For example, structured data is used for recommendation systems, while unstructured data (such as images and voice data) is used for deep learning models.
3. Big Data and Analytics
- Structured data is crucial for dashboards, KPIs, and real-time reports.
- Unstructured data is processed using Hadoop, Apache Spark, and AI-driven tools for insights.
4. Cloud Computing and Data Storage
- Cloud services like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure provide solutions for storing and analyzing both structured and unstructured data.
Conclusion
Both structured and unstructured data are vital for different applications. Structured data is easier to manage and analyze but lacks flexibility, whereas unstructured data holds vast potential for insights but requires advanced processing techniques. Businesses, researchers, and AI developers must understand these differences to make data-driven decisions effectively.
Want to start a career in Data Science?
The Post Graduate Program in Data Science from UT Austin in collaboration with Great Learning covers essential data science concepts through a comprehensive curriculum—from basic to advanced courses—that fully equips you for a successful data science career. Enroll Now!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How is structured data used in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)?
Structured data is used in AI and ML for predictive analytics, recommendation systems, and automation. It provides well-organized, labeled datasets that help in model training and performance optimization.
2. What are the challenges of handling unstructured data?
The main challenges include high storage requirements, difficulty in searching and retrieving data, and the need for advanced tools like AI, NLP, and big data analytics to process it effectively.
3. Can structured and unstructured data be combined for analysis?
Yes, businesses often integrate both types of data for deeper insights. For example, structured sales data can be combined with customer reviews (unstructured) to analyze buying behavior.
4. Which industries rely heavily on unstructured data?
Industries such as healthcare (medical imaging, patient records), social media (posts, videos, comments), and cybersecurity (network logs, security footage) rely extensively on unstructured data for insights and operations.
5. What are the future trends in structured and unstructured data management?
Future trends include AI-driven data processing, advanced cloud storage solutions, and hybrid databases that support both structured and unstructured data for seamless integration and analysis.