What is Product life cycle management?

Product life cycle management covers all the aspects of the product, from its conceptualization to its disposal. It is an umbrella term and has different meanings for different organisations. It refers to the management of the product as it goes through various stages like introduction, development, deployment, etc. It involves both manufacturing and the marketing of the product. It has been a boon to product managers to make important product decisions ranging from the budget and its implementation strategy.
Why do we need Product life cycle management?
Organisations that manufacture goods face numerous issues during business processes like manufacturing and integration, etc. Product life cycle management(PLM) was designed to mitigate these issues, to help engineers collaborate on product designs. It was designed to help control information across the lifecycle of the product and to make it accessible to teams across the organization. PLM has helped organisations cope up with increasing engineering challenges and complexity while developing new products.
PLM has led to effective streamlining of the business processes. Since its inception, the main aim of PLM has been to help the business produce a product that outperforms its competitors, generates high profits and lasts as long as there’s demand for it.
The evolution of PLM
Product life cycle management as an implementation came into existence in 1985. American Motors Corporation(AMC) was looking into speeding up their production processes to have the edge over their competitors. As a part of this implementation, they introduced CAD( Computer-Aided Design) and new communication systems, which made their engineers more efficient and productive. AMC was later on acquired by Chrysler, who in turn expanded the PLM system to become the lowest-cost producer of the auto industry by the mid-1990s. PLM was first designed by keeping the engineers in mind. It did not allow for customer transparency or responsiveness. This led to the introduction of a next-generation PLM or Cloud-based PLM.
Cloud-Based Product Lifecycle Management
Cloud-based PLM software has made it easier to develop complex products with even greater product quality. Since it provides a single source of truth through the cloud, it’s easier to track data and processes. It updates product changes, industry compliances, advancements in real-time. This allows for a timely and efficient collaboration across all departments involved, regardless of their location. It has truly helped speed up and improve product development. Product lifecycle management has been a boon for the COVID world, where most of the workforce is working remotely.
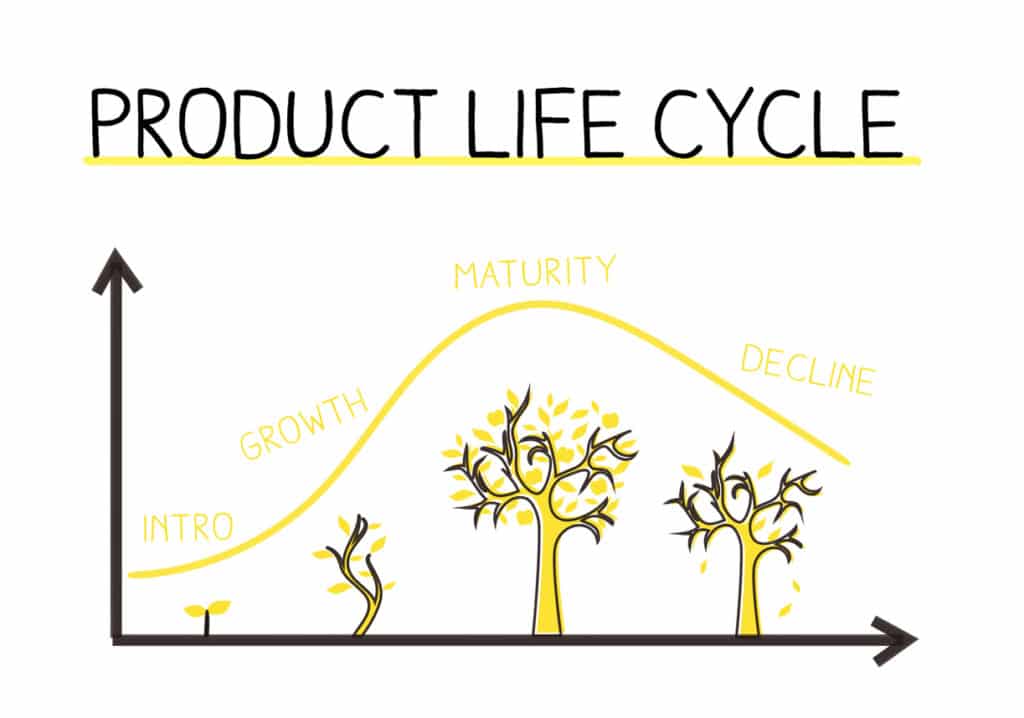
Top Stages of PLM
The lifecycle of a product generally begins with an Idea. Later, it thickens into a design to finally transition into the manufacturing stage to be given to the world. To put it correctly, there are four important stages to a product lifecycle. Every product has to go through these stages and the finer-grained processes in between like marketing, engineering, etc.
The four important stages are:
- Introduction: For a company launching a new product, this is the most expensive stage. The market size for the product is small, which leads to low sales. This will increase in the coming days. However, the cost for research and development, launch marketing, etc., could be quite high.
- Growth: In this stage, there’s a portrayal of a significant increase in sales and profits. This leads to scaling of production, which in turn leads to more profits. This, in turn, makes the business promote the product and make it reach its potential in the market.
- Maturity: In a product’s maturity stage, the product is established in the market. The only aim here is to maintain the market share. The should be wise modifications or improvements in the product to maintain a competitive advantage.
- Decline: In this stage, the market for the product starts to decline. The causes could be a saturation in the market or the market shifting towards a different product. This could be an inevitable stage, but it is possible for the company to still make some profit by switching to cheaper markets or less expensive production methods.
The Difference Between The Product Life Cycle And The Project Life Cycle
A project life cycle is an action map that lays out the steps or milestones needed to be completed to achieve target-specific results. In contrast, a product lifecycle is a map of where the product sales are and what place they would be in some time.
Benefits of Product Life cycle Management
The benefits of PLM are:
- Improved product quality and designs.
- Reduced prototyping costs and marketing time.
- Quick identification of revenue contributions and sales opportunities.
- Improvements to engineering efficiency and development.
- Savings through the reusability of data.
- Highly efficient product optimization framework.
- Improved project delivery and the ability to manage seasonal fluctuation
- Improved forecasting to reduce costs.
- Supply chain collaboration is maximized.
Conclusion
Today, Product Lifecycle Management has been adopted across manufacturing to boost innovation, foster collaboration. It has efficiently helped support growth through designing based on customer demand and helped in product individualization. And in a time of digital transformation, Forbes predicted that due to the COVID-19 pandemic, manufacturing would experience five years of innovation in the next 18 months. PLM will play a crucial role in helping companies get products to market faster. Also, with the PLM cloud software, most of the smaller companies will get access to it and will continue to drive collaboration.









