Welcome to our comprehensive guide for acing your Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) interviews in 2024!
In this article, we’ve curated the top 70 OOPs interview questions and answers to help you master the most critical concepts and techniques.
Whether you’re brushing up on your OOP viva questions or gearing up for a career-defining interview, these selected object oriented programming interview questions cover everything from basic principles to advanced topics.
Top 10 OOPs Interview Questions in 2024
Great Learning has compiled the top 10 Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) interview questions commonly encountered during interviews.
- What is OOPs?
- What is the difference between Procedural programming and OOPs?
- Why use OOPs?
- What are the basic concepts of OOPs?
- What is Encapsulation?
- What is Abstraction?
- What is method overloading?
- What is method overriding?
- Types of Inheritance in OOPS
- What is an object?
This blog is further divided into 3 different sections, they are :
- Basic OOPs concepts interview questions
- OOPs Interview Questions for Experienced
- Frequently Asked OOP interview questions
Let’s dive in
Basic OOPs Interview Questions
1. What is OOPs?
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming approach that employs classes and objects to organize software programs into reusable code templates.
Languages such as Java, C++, Python, and JavaScript support OOP by facilitating the creation of classes that specify attributes and methods, while objects are instances of these classes.
OOP principles encompass inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, and abstraction, facilitating the representation of real-world entities in software design.
Don’t just learn Java; master it with our free “OOPS in Java Free Course.”
2. Difference between Procedural programming and OOPs?
| Procedural Programming | Oops |
| Procedural Programming is based on functions. | Object-oriented programming is based on real-world objects. |
| It shows the data to the entire program. | It encapsulates the data. |
| It does not have a scope for code reuse. | It provides more scope for code reuse. |
| It follows the concept of top-down programming. | It follows a bottom-up programming paradigm. |
| The nature of the language is complicated. | It is less complicated in nature, so it is easier to modify, extend and maintain. |
| It is hard to modify, extend and maintain the code. |
3. Why use OOPs?
Modularity: OOP promotes modular design, making dividing complex problems into smaller, manageable parts easier.
Reusability: With OOP, you can use classes and objects repeatedly in different parts of a program or other programs, saving time and making programs more efficient.
Encapsulation: Encapsulation hides the inner workings of an object and only shows what’s necessary, which keeps things secure and prevents accidental changes.
Inheritance: OOP lets you create new classes based on existing ones, which helps reuse code and build organized relationships between classes.
Polymorphism: OOP allows different objects to be treated as belonging to the same group, making software more flexible and more accessible to expand.
Abstraction: OOP simplifies real-world things into easier-to-understand models, focusing on what’s essential and hiding unnecessary details.
4. What are the basic features of OOPs?
The basic features of OOPs are:
- Inheritance
- Encapsulation
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
5. What is Encapsulation?
Encapsulation in object-oriented programming involves bundling data and methods within a class, restricting direct access to the data from outside the class. This concept offers several benefits:
Data Protection: Encapsulation shields data from unauthorized access, preventing unintended modification and ensuring data integrity.
Modularity: It promotes modular design by encapsulating related data and methods within a single unit, enhancing code organization and maintainability.
Simplified Interface: Encapsulation provides a straightforward interface for interacting with objects, allowing users to focus on the functionality rather than the implementation details.
Flexibility: By hiding internal implementation details, encapsulation enables developers to modify the internal structure of a class without affecting its external interface, promoting code reuse and reducing dependencies.
6. What is Abstraction?
Abstraction in object-oriented programming involves simplifying complex systems by focusing on essential characteristics while hiding unnecessary details. It allows developers to create models that represent real-world entities more understandably.
class Car:
def __init__(self, make, model, year):
self.make = make
self.model = model
self.year = year
def start_engine(self):
# Code to start the car's engine
pass
def drive(self):
# Code to drive the car
pass
# Creating an instance of the Car class
my_car = Car("Toyota", "Camry", 2022)
In this example, the ‘Car’ class represents the abstraction of a car.
It encapsulates a car’s essential attributes and behaviors, such as its make, model, and year, as well as methods like ‘start_engine()’ and ‘drive().’
This abstraction allows us to work with cars in our code without needing to understand all the intricate details of how they work internally.
7. What is method overloading?
Method overloading is a feature in object-oriented programming that allows a class to have multiple methods with the same name but different parameters or parameter types.
This enables developers to define various versions of a technique, each tailored to accept other types or numbers of parameters.
When a method is called, the appropriate version is selected based on the parameters provided.
For example, consider a Calculator class with an add() method:
public class Calculator {
public int add(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
public double add(double num1, double num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
}
In this example, the add() method is overloaded to accept integer and double parameters.
Depending on whether integer or double values are passed as arguments, the corresponding version of the add() method will be invoked.
This allows for flexibility and convenience when working with different data types.
8. What is method overriding?
Method overriding is a concept in object-oriented programming where a subclass provides a specific implementation of a method already defined in its superclass. This means that the subclass redefines the behavior of the method inherited from the superclass.
Key points about method overriding:
- Method overriding occurs when a subclass implements a method already defined in its superclass.
- The method signature (name and parameters) in the subclass must match the superclass’s method signature.
- Method overriding implements polymorphism, in which a subclass object can be treated as an object of its superclass but with its own specialized behavior.
- Method overriding allows for the customization of behavior in subclasses, providing flexibility and extensibility in object-oriented design.
9. Types of Inheritance in OOPS
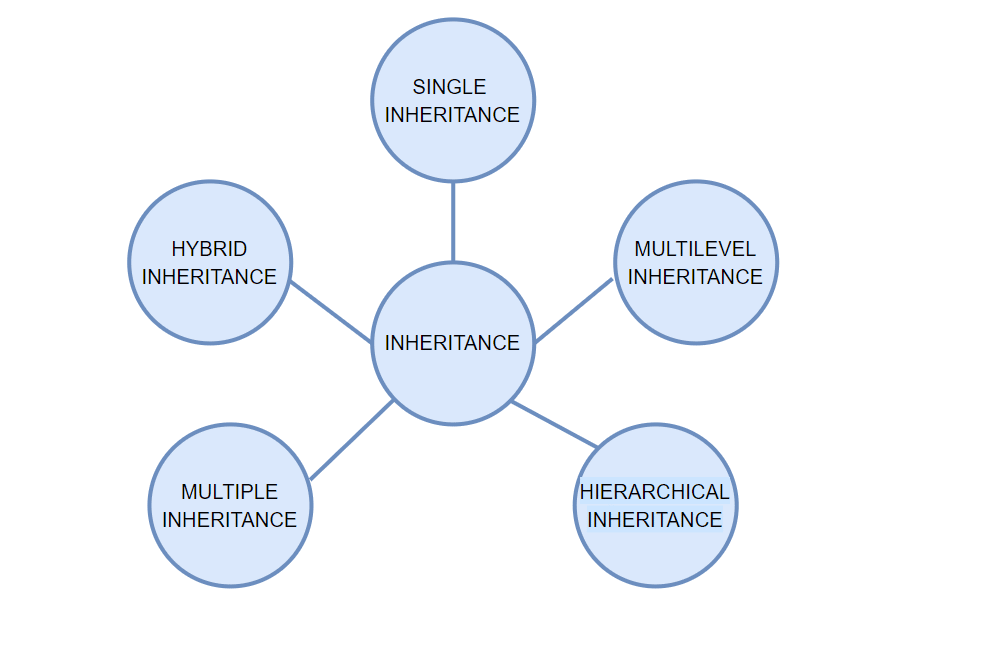
- Single Inheritance: Child class derived directly from the base class.
- Multiple Inheritance: A child class inherits from more than one base class.
- Multi-level Inheritance: The child class is derived from a parent class, which is further derived from another class.
- Multi-path Inheritance: A child class inherits from two or more classes with a standard base class.
- Hierarchical Inheritance: Multiple derived classes are created from a single base class.
- Hybrid Inheritance: Combination of two or more types of inheritance.
10. What are the primary characteristics of OOPs?
The main characteristics of OOPs are given as follows:
- In OOP, you combine the code into one unit so you can specify the parameters of each piece of data. This process of wrapping up data into a single unit is called encapsulation.
- By using classes, you can generalise your object types and make your application easier to use. This is termed as an abstraction.
- The ability for a class to inherit characteristics and behaviours from another class allows for more code reuse.
- Polymorphism allows for the creation of several objects from a single, adaptable class of code.
11. Is it possible to call the base class method without creating an instance?
Yes, we can possibly call the base class method without creating an instance in the following 3 cases:
- If the method is static
- Calling the inherited method inside a derived class
- Calling the method using the base keyword from the sub-classes
The most popular case is that of the static methods.
12. What are the limitations of OOPs?
Not Ideal for Small Problems: OOP may be overly complex for small-scale projects, leading to unnecessary overhead.
Requires Extensive Testing: OOP code often requires thorough testing to ensure proper functionality due to its complexity.
Time-Consuming: Developing OOP solutions may take longer due to the need to plan and design object structures.
Necessitates Proper Planning: Effective use of OOP requires careful upfront planning to define classes, relationships, and interactions.
Shift in Thinking: Programmers must adopt a mindset focused on object-oriented problem-solving, which may require a learning curve and mindset shift.
13. What are constructors?
Constructors are unique methods in a class that are automatically called when an instance of the class is created. They are used to initialize the object’s state or perform any necessary setup operations.
14. Types of constructor
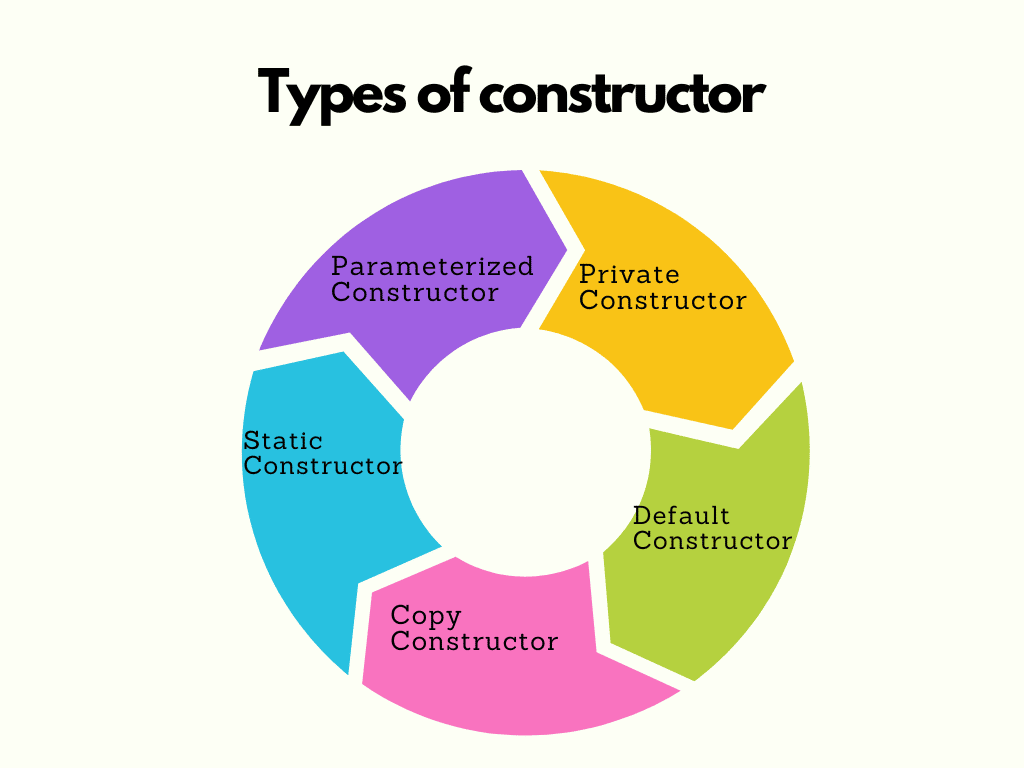
Private Constructor: This restricts the instantiation of a class from outside. It is typically used for utility classes with static methods.
Default Constructor: If no constructor is explicitly defined, it is automatically generated by the compiler and initializes instance variables to default values.
Copy Constructor: This function creates a new object by copying the state of an existing object. It is used for creating deep copies or clones.
Static Constructor: Initializes static data members or performs one-time setup tasks for the class, executed only once when the class is loaded.
Parameterized Constructor: Accepts parameters to initialize instance variables during object creation, allowing customization of object state.
15. What is the difference between a class and a structure?
Class: A class is like a blueprint for creating objects in object-oriented programming (OOP). It combines data and behavior into a single unit. Objects made from a class are instances of that class, each with its own data set. Classes are essential for modeling real-world concepts and implementing OOP features like inheritance and polymorphism.
Structure: A structure is a way to group variables of different types under a single name. It’s commonly used in languages like C to define custom data types holding multiple elements. Unlike classes, structures don’t support methods or inheritance. They’re mainly used to organize related data for easier management and manipulation within a program.
16. What are the access modifiers?
Access modifiers are keywords used in object-oriented programming languages to control the visibility and accessibility of classes, methods, and other members within a program.
They determine how these members can be accessed from different parts of the program or outside modules. The primary access modifiers include:
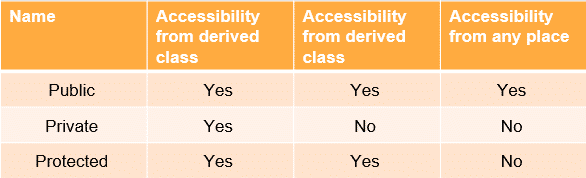
Public: Allows members to be accessed from any part of the program.
Private: Restricts access to members within the same class, preventing access from outside.
Protected: Grants access to members within the same class and its subclasses, but not from outside.
Internal: Limits access to members within the same assembly or module.
Protected Internal: Combines the behavior of protected and internal, allowing access within the same assembly or from subclasses, whether in the same assembly or not.
These access modifiers help enforce encapsulation, control members’ visibility and maintain the integrity of the program’s design.
17. What languages come under the oops concept?
Simula is known as the first object-oriented programming language, the most popular OOP languages are:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
- Visual Basic
- .NET
- Ruby
- Scala
- PHP
Check out the OOPs concept in Python Video.
18. What is inheritance?
Whenever one class is derived from another, it is referred to as inheritance. The child class will inherit all of the parent class’s public and protected properties and methods. Apart from the attributes and methods inherited from the parent class, it can also have its own additional set of features. The’ extends’ keyword is used to specify an inherited class.
If you derive a class from another class that is known as inheritance. The child class will inherit all the public and protected properties and methods from the parent class. The child class can also have its own properties and methods. An inherited class is defined by using the extends keyword.
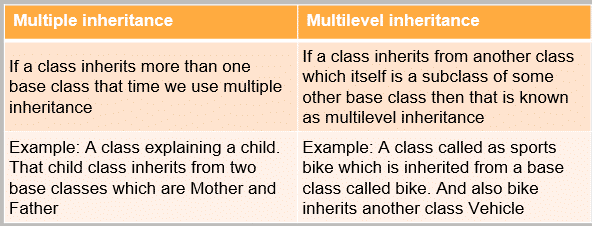
19. What is hybrid inheritance?
The type of inheritance formed by the combination of different types of inheritances like single, multiple inheritances, etc. is classified as hybrid inheritance.
20. What is hierarchical inheritance?
In the case of a hierarchical inheritance, multiple subclasses inherit from a parent class. Hierarchical inheritance is a type of inheritance in which multiple classes are descended from a single parent or base class. For example, the fruit class can have ‘apple’, ’mango’, ’banana’, ‘cherry’ etc. as its subclasses.
21. What are the limitations of inheritance?
Inflexibility: Inheritance creates a rigid relationship between classes, making it challenging to change the hierarchy once established.
Complexity: Deep inheritance hierarchies can lead to complex and difficult-to-understand code, especially when multiple levels of inheritance are involved.
Tight Coupling: Subclasses become tightly coupled to their superclasses, increasing dependencies and making modifying or extending the system harder.
Code Reusability Issues: Over-reliance on inheritance for code reuse can lead to duplication and maintenance difficulties.
Violation of Encapsulation: Inherited members are not encapsulated within the subclass, potentially allowing unintended access or modification.
Diamond Problem: In languages supporting multiple inheritance, such as C++, the diamond problem can occur, leading to ambiguity and conflicts in method resolution.
22. What is a superclass?
A superclass is a class from which a subclass or child class is derived. Base class and parent class are other names for a superclass. For example, if Student is a class derived from the Person class, then the Person class will be referred to as the superclass.
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def greet(self):
print("Hello, my name is", self.name, "and I am", self.age, "years old.")
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self, name, age, student_id):
super().__init__(name, age)
self.student_id = student_id
def study(self):
print(self.name, "is studying.")
# Creating an instance of the Student class
student = Student("Alice", 20, "12345")
student.greet() # Output: Hello, my name is Alice and I am 20 years old.
student.study() # Output: Alice is studying.
In this example, the ‘Person’ class serves as the superclass, providing common attributes like ‘name’ and ‘age’ and a method ‘greet()’. The ‘Student’ class is a subclass derived from ‘Person’, inheriting its properties and methods.
The ‘Student’ class also defines its method of ‘study'(). Instances of the ‘Student’ class can access both ‘Person’ class methods, like ‘greet()’, and its own methods, like ‘study()’.
23. What is a subclass?
A subclass is a class that inherits properties and behaviors from another class, known as its superclass or parent class. It extends or specializes in the functionality of its superclass. For example:
class Vehicle:
def __init__(self, brand):
self.brand = brand
def drive(self):
print("Driving a", self.brand)
class Car(Vehicle):
def __init__(self, brand, model):
super().__init__(brand)
self.model = model
def honk(self):
print("Honking the horn of", self.brand, self.model)
# Creating an instance of the Car class
my_car = Car("Toyota", "Camry")
my_car.drive() # Output: Driving a Toyota
my_car.honk() # Output: Honking the horn of Toyota Camry
In this example, the ‘Car’ class is a subclass of the ‘Vehicle’ class. It inherits the ‘drive()’ method from Vehicle and adds its method ‘honk()’. Instances of the Car class have access to both superclass and subclass methods.
Curious about Object-Oriented Programming in Python?
Discover the Fundamentals of OOP concepts in Python in our blog!
24. What is Polymorphism?
Polymorphism is one of the most used and core concepts in OOP languages. It explains the concept of different classes can be used with the same interface. Each of these classes can have its own implementation of the interface.
25. What is static polymorphism?
Static polymorphism, also known as compile-time polymorphism or method overloading, occurs when multiple methods in the same class have the same name but different parameters.
The appropriate execution method is determined at compile time based on the number or type of arguments passed to the process.
26. What is dynamic polymorphism?
Dynamic polymorphism is a method or process that handles a call to an overridden method during runtime rather than at compile time. It is also referred to as dynamic method dispatch or runtime polymorphism. Using method overriding, we can create dynamic polymorphism. An example of runtime polymorphism: is method overriding.
27. What is operator overloading?
Operator overloading is a feature in object-oriented programming that allows operators to be redefined for custom types. It enables objects to behave like built-in data types with operators such as +, -, *, /, etc.
By overloading operators, programmers can define how operators should work with their custom classes or structures, providing more intuitive and natural syntax for operations involving user-defined types.
Learn more about Java method overloading with examples in our comprehensive guide on Method Overloading In Java.
Also
Discover key concepts and real-world applications in “Operator Overloading in C++ with examples“.
28. Differentiate between overloading and overriding.
When two or more methods in the same class have the same name but different parameters, this is referred to as overloading. The technique of using the same method signature, i.e., name and parameters, in both the superclass and the child class is known as overriding.

29. What is encapsulation?
Encapsulation in object-oriented programming involves bundling data (attributes or variables) and methods (functions or procedures) that operate on the data into a single unit or class.
This concept allows for data hiding, where the internal state of an object is hidden from the outside world and can only be accessed through designated methods.
This promotes better code organization, security, and maintainability by preventing direct access to sensitive data and enforcing controlled access through well-defined interfaces.
30. What is the difference between public, private and protected access modifiers?
31. What is data abstraction?
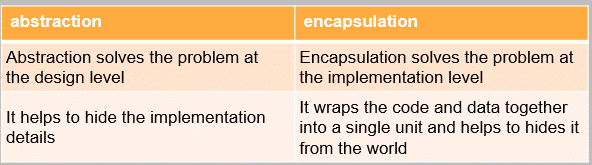
Data abstraction is indeed a crucial feature of object-oriented programming. It involves showing only essential information while hiding the implementation details.
For instance, when using a mobile phone, you know how to message or call someone, but you don’t need to know the intricate technical processes behind it.
This exemplifies data abstraction as it shields users from unnecessary complexities, focusing on the actions they can perform without burdening them with implementation specifics.
32. How to achieve data abstraction?
Data abstraction can be achieved using two ways:
- Abstract class
- Abstract method
33. What is an abstract class?
An abstract class is also a class which is consists of abstract methods.
So what is an abstract method?
These methods are basically declared but not defined and If these methods need to be used later in some subclass that time those methods have to be exclusively defined in the subclass.
34. Differentiate between data abstraction and encapsulation.
35. What are virtual functions?
Virtual functions are declared in a base class that derived classes can override. They allow dynamic polymorphism, enabling selecting the appropriate function implementation at runtime based on the object’s type.
In languages like C++, virtual functions are used to achieve late binding or runtime polymorphism.
Explore the principles of object-oriented programming in C++ with our free OOPs Concepts in C++ course.
36. What is a destructor?
A destructor is a unique method in object-oriented programming that is automatically called when an object is destroyed or goes out of scope.
Its primary purpose is to release any resources or memory allocated by the object during its lifetime, such as closing files, releasing database connections, or deallocating dynamic memory.
This helps in proper memory management and resource cleanup in the program.
37. What is a copy constructor?
By copying the members of an existing object, the copy constructor initialises the members of a newly formed object. The argument for the copy constructor is a reference to an object of the same class. Programmers have the option of directly defining the copy constructor. The compiler defines the copy constructor if the programmer doesn’t.
Don’t miss out on mastering copy constructors in C++!
Explore our blog on “Copy Constructor in C++ – Everything You Need To Know” and enhance your expertise.
38. What is the use of ‘finalize’?
The finalize() method in object-oriented programming performs cleanup operations on an object before it is garbage collected. It helps release unmanaged resources held by the object, such as file handles or network connections, aiding in memory management.
39. What is Garbage Collection(GC)?
Garbage Collection (GC) is a memory management feature in object-oriented programming languages like C# and Java. It automatically releases memory space reserved for objects no longer in use by the application.
OOP languages with garbage collection utilize GC engines to reclaim memory allocated to objects no longer referenced, ensuring efficient memory usage and preventing memory leaks.
40. What is a final variable?
A final object-oriented programming (OOP) variable can only be initialized once and cannot be reassigned to a different object after its initial assignment. When a variable is marked as final, its reference cannot change, meaning it always refers to the same object in memory.
However, the object’s state, such as its data fields, can still be modified. This ensures that the reference to the object remains constant throughout the program, promoting immutability and guaranteeing consistency in object-oriented design.
41. What is an exception?
An exception is a kind of message that interrupts and comes up when there is an issue with the normal execution of a program. Exceptions provide an error and transfer it to the exception handler to resolve it. The state of the program is saved as soon as an exception is raised.
42. What is exception handling?
Exception handling in object-oriented programming is a fundamental concept used to manage errors and exceptional situations that may arise during program execution.
It uses try, catch, and throw keywords to detect, handle, and recover from errors gracefully, preventing program crashes and ensuring robustness.
When an error occurs, an exception object is thrown, and the program flow is redirected to the nearest enclosing catch block that matches the thrown exception type, allowing for appropriate error handling and recovery strategies.
43. What is the difference between an error and an exception?

44. What is a try/ catch block?
The terms “try” and “catch” describe how to handle exceptions brought on by coding or data mistakes while a program is running. The section of code where exceptions occur is called a try block. Exceptions from try blocks are caught and handled in a catch block.
45. What is a finally block?
Finally designates the section of code that works with the try keyword. It specifies code that is always executed before the method is finished, immediately behind the try and any catch blocks. Regardless of whether an exception is thrown or caught, the finally block is always executed.
46. Can you call the base class method without creating an instance?
Yes, you are allowed to call the base class without instantiating it but there are some conditions that are applicable:
- If it is a static method
- The base class is inherited by some other subclass
47. What is the difference between OOP and SOP?
The critical distinction between Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and Procedural Programming (also known as Structured Programming) lies in their approach to program organization and design:
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):
Involves the creation of programs using a collection of objects and their interactions. It emphasizes concepts of objects and classes, where everything is considered as an object with specific properties and behaviors represented in classes. OOP provides encapsulation and abstraction in the code, enabling modular and reusable design. Examples include languages like Java.
Procedural Programming (SOP):
Involves creating programs using a collection of modules or functions. It focuses on functions and structures, where everything is considered functionality and structures, represented using functions. Procedural programming languages, like C, organize code based on procedures or routines, with less emphasis on data and its organization within objects.
48. What is the difference between a class and an object?
In object-oriented programming (OOP), the key difference between a class and an object lies in their roles and definitions:
Class:
A class is a blueprint or template for creating objects. It defines the properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods) that all objects of that class will have. Classes serve as the foundation for object creation and encapsulate the common characteristics shared by multiple objects.
Object:
An object is an instance of a class. It represents a specific entity or instance in memory that conforms to the structure defined by its class. Objects have their unique state (attribute values) and behavior (method executions) based on the class from which they were instantiated.
class Car:
def __init__(self, brand, model):
self.brand = brand
self.model = model
def drive(self):
print("Driving", self.brand, self.model)
# Creating an object (instance) of the Car class
my_car = Car("Toyota", "Camry")
# Accessing attributes and invoking methods of the object
print(my_car.brand) # Output: Toyota
print(my_car.model) # Output: Camry
my_car.drive() # Output: Driving Toyota Camry
In this example, ‘Car’ is a class that defines the blueprint for creating cars. ‘my_car’ is an object (instance) of the ‘Car’ class, representing a specific car entity with its brand and model attributes. The object can access methods like drive() defined in its class.
49. What are ‘access specifiers’?
In object-oriented programming, access specifiers are keywords used to control the visibility and accessibility of class members, such as attributes and methods. They specify the level of access that other classes or code modules have to these members.
In most OOP languages, the primary access specifiers include:
Public: Allows unrestricted access to class members from anywhere in the program.
Private: This option restricts access to class members only within the class where they are declared, preventing access from outside.
Protected: Allows access to class members within the class where they are declared and in its subclasses, but not from outside.
These access specifiers help enforce encapsulation, define the boundaries of class members, and maintain the integrity of the program’s design.
50. Can you create an instance of an abstract class?
No, an instance of the Abstract class cannot be created. To implement the abstract Class, abstract methods, the Abstract Class should be extended by another class, and the object of the implementation class can be created.
OOPs Interview Questions for Experienced
51. What is an interface?
An interface is a user-defined data type and is a collection of abstract methods. A class implements an interface, thereby inheriting the abstract methods of the interface. A class describes an object’s attributes and behaviours, and an interface contains behaviours that a class implements. The Class represents “how,” and the interface represents “what’.
52. What are pure virtual functions?
A pure virtual function/method is a function whose implementations are not provided in the base class, and only a declaration is provided. The pure virtual function can have its implementation code in the derived class; otherwise, the derived class will also be considered an abstract Class. The Class containing pure virtual functions is abstract.
53. Differentiate between a class and a method.
A class is a blueprint of objects, and it consists of the properties and behaviour of the objects.
Methods are programming constructs that perform specific tasks/behaviour.
54. Differentiate between an abstract class and an interface?
An interface can have only abstract methods, but an Abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods.
The interface should be used if just the requirement specification is known and nothing about implementation. If the implementation is known, but partially, then an abstract class should be used. If the implementation is known completely, then a concrete Class should be used.
55. What is the virtual function?
A virtual function is declared within a base class that can be overridden in derived classes. This enables polymorphic behavior, where the appropriate function implementation is selected based on the object type during runtime.
56. What are the characteristics of an abstract class?
- A class having at least one pure virtual function is called an Abstract class.
- An Abstract class cannot have objects created, i.e., an abstract class cannot be instantiated, but Object references can be created.
- An Abstract class can have non-abstract functions and pure virtual functions also.
- The pure virtual function can have its implementation code in the derived class; otherwise, the derived class will also be considered an abstract Class
57. What is constructor chaining?
Constructor chaining is a method to call one constructor from another concerning a current object reference. It can be done in two ways: –
- Using the “this” keyword, the reference can be made to the constructor in the current class.
- To call the constructor from the base class “super” keyword will be used.
58. What is Coupling in OOP, and why is it helpful?
The degree of dependency between the components is called coupling.
Types of Coupling
A. Tight Coupling – If the dependency between components is high, these components are called tightly coupled.
Ex: – Below three Classes are highly dependent on each other hence they are tightly coupled.
class P
{
static int a = Q.j;
}
class Q
{
static int j = R.method();
}
class R
{
public static int method(){
return 3;
}
B. Loose Coupling – If the dependency between components is low, it is called loose coupling. Loose coupling is preferred because of the following reasons:-
- It increases the maintainability of code
- It provides reusability of code
59. Name the operators that cannot be overloaded
The operators that cannot be overloaded typically include:
. (dot) member selection operator
.* member selection with a pointer to the object operator (in C++)
:: scope resolution operator
?: ternary operator
Additionally, in languages like Java, operators such as &&, ||, and ?: cannot be overloaded.
The + operator can be overloaded in many programming languages, such as C++ and C#.
60. What is Cohesion in OOP?
Cohesion in object-oriented programming refers to the degree to which elements within a module (such as a class) are related and serve a common purpose. Higher cohesion indicates that the elements within the module are closely related and focused on a specific task or functionality.
Advantages of high cohesion include improved code maintainability and reuse because modules with well-defined and specific functionality are easier to understand, modify, and reuse in different parts of the program or in other programs.
61. What are the levels of data abstraction?
Levels of data abstraction refer to the different layers of abstraction within a software system, ranging from low-level implementation details to high-level conceptual models.
Abstraction is achieved through abstract classes, interfaces, and encapsulation, which hide complexity and provide simplified interfaces for interacting with data and functionality.
These levels of abstraction help manage complexity, improve maintainability, and facilitate modular design in software development.
62. What are the types of variables in OOP?
Variables are basic units to store data in RAM for Java programs.
Variables should be declared before using them in Java programming. Variable initialization can be static or dynamic. The syntax for variable declaration and static initialization is: –
Types of variables
- Primitive Variables: It is used to represent primitive values like int, float, etc.
- Reference Variables: It is used to refer to objects in Java.
- Instance Variables: Variables whose value varied from object to object are instance variables. For every object, a separate copy of the instance variable is created. Instance variables are declared within the Class and outside any method/block/constructor
- Static variables: For static Variables, a single copy of the variable is created, and that copy is shared between every Class object. The static variable is created during class loading and destroyed at class unloading.
- Static variables can be accessed directly from the static and instance area. We are not required to perform initialization explicitly for static variables, and JVM will provide default values.
- Local Variables: Variables declared inside a method or block or constructor are local variables. Hence the scope of local variables is the same as the block’s scope in which we declared that variable.
JVM doesn’t provide default values, and before using that variable, the initialization should be performed explicitly.
63. What do you understand by Garbage Collection in the OOPs world?
Garbage collection is a memory recovery technique included in programming languages like C# and Java. A GC-enabled programming language contains one or more garbage collectors that automatically free up memory space allocated to objects that are no longer needed by the program.
64. Is it possible to run a Java application without implementing the OOPs concept?
No, since Java programmes are founded on the concept of object-oriented programming models, or OOPs, a Java application cannot be implemented without it.
Understand the fundamentals of Object-Oriented Programming in Java!
Our blog, “OOPs Concept in Java with Examples,” offers real-world examples and practical insights.
65. What is the output of the below code?
class Person
{
private String show()
{
return "This is a person";
}
}
class Teacher extends Person
{
protected String show()
{
return "This is a teacher";
}
}
public class MathsTeacher extends Person
{
@Override public final String show()
{
return "This is a Maths teacher";
}
public static void main(String[] name)
{
final Person mt = new MathsTeacher();
System.out.print(mt.show());
}
}
The output will be: This is a Maths teacher
66. Find the output of the below code.
class Arithmetic
{
public final double var = 5;
}
class DeepArith extends Arithmetic
{
public final double var = 10;
}
public class AdvancedArith extends DeepArith
{
public final double secret = 20;
public static void main(String[] num)
{
Arithmetic arith = new AdvancedArith();
System.out.print(arith.var);
}
}
The correct output for this code is 5.
67. Predict the output of the following.
class Parent
{
public void display()
{
System.out.println("Parent");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{ private void display()
{ System.out.println("Child");
}
}
public class main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Parent node = new Child(); node.show();
}
}
Running this code will generate a compile error as a sub-class function overriding a super class function cannot be given more restrictive access.
68. Implement a Singleton class in Java.
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {
// Private constructor to prevent instantiation.
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
69. Implement a Stack data structure using a LinkedList in Python.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def is_empty(self):
return self.head is None
def push(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
raise Exception("Stack is empty")
popped_value = self.head.data
self.head = self.head.next
return popped_value
70. Implement an abstract class in C# with an abstract method.
abstract class Shape
{
public abstract double CalculateArea();
}
class Circle : Shape
{
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius)
{
this.radius = radius;
}
public override double CalculateArea()
{
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
Conclusion
This compilation of top OOPs interview questions and answers will be valuable for your upcoming interviews or viva sessions. Mastering object-oriented programming is gradual, and practical application is crucial in solidifying your understanding. To further enhance your skills, explore free online courses for object-oriented programming that can help deepen your knowledge and improve your practical application of these concepts.
To delve deeper into the real-world applications of OOPs, consider enrolling in courses like the Free Python Fundamentals Course for Beginners and the Free Java Programming Course with Certificate offered by Great Learning.
These courses provide hands-on experience and insights into applying OOP principles, helping you to strengthen your skills and prepare you for various job interviews and practical scenarios.
Frequently Asked OOPs Interview Questions
OOP stands for Object-Oriented Programming, and its four basic principles are Encapsulation, Abstraction, Polymorphism, and Inheritance. OOP enables programmers to consider software development as if they are working with actual entities. In OOP, some objects have a field where data/knowledge can be stored and can do several methods.
Object-Oriented Programming, also usually called OOPS, is a kind of programming that is more object-based and not just based on functions or procedures. Individual objects are collected into several classes. Real-world entities such as inheritance, polymorphism, and hiding are implemented by OOPS into programming. It also enables binding data as well as code together.
The three main principles of Object-Oriented Programming are Encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
OOPS or Object-Oriented Programming System is a programming concept that mainly works based on Encapsulation, Abstraction, Polymorphism, and Inheritance. The usual concept of OOPs is to create objects, use them again all through the program, and finally manipulate these objects to fetch our results.
The main aim of an Object-Oriented Programming System is to implement real-world entities such as polymorphism, inheritance, hiding, and many more in programming. The aim lies in binding together the data as well as functions that work on them so that other parts of the code cannot access the data other than that function.
Polymorphism in an Object-Oriented Programming System is a feature of object-based programming languages that enable a particular routine to use variables of several types at different times. It can also be called the ability of a programming language to present the same interface for different primary data types.
The father of the Object-Oriented Programming System is considered to be Alan Kay by some people. He identified some characteristics as basics to OOP Kay 1993:1. He coined OOPs around 1966 or 1967 when he was at grad school.
Some of the main features in OOPS include Classes, Objects, Data Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, and Polymorphism. OOP is a programming paradigm that is based on the idea of objects.
Since OOP is one of the main development approaches which is easily accepted, the advantages are many. Some of the advantages of OOPS include Reusability, Data Redundancy, Code Maintenance, Security, Design Benefits, Easy Troubleshooting, Better Productivity, Polymorphism Flexibility, and Problem-solving.
If you wish to learn more about such concepts, you can join a Software Engineering courses that will help you upskill.