Working with Java and storing key-value pairs, but confused about choosing between HashMap and HashTable?
Don't worry; this article will help you better understand the differences between HashMap and HashTable. Both are fundamental data structures which use hash-based storage for key-value pairs.
However, they cater to different needs. They provide functionalities like the capability to work on multi-threaded applications and the fastest way to retrieve data. Understanding the difference between the two is essential to know the specific usage of HashMap and HashTable.
What is a HashMap?
A HashMap in Java is a widely used data structure known for its implementation in the Map interface. Ideal for single-threaded applications where synchronization is handled externally. It provides constant time performance for most operations like insertion and retrieval. It stores data in key-value pairs and is known for its speedy results.
Imagine a library which has approximately 70 categories of books. Each category contains approximately 200 books and has a barcode.
Instead of searching category shelves endlessly, we can scan the barcode and track the book's location. That's precisely how a HashMap works. It maps keys, in our case, the barcodes to values and, in our case, the location of books.
Features of HashMap:
- Allow null keys and values: in the HashMap, you can have a single null key and multiple null values.
- Not synchronized: it is efficient for single-threaded applications and does not handle multiple-threaded applications simultaneously.
- High performance: in environments where synchronization is not required, it has high performance and fast speed.
Syntax
HashMap<K, V> map = new HashMap<>();
Where K = type of keys and V= type of values.
Example
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a HashMap
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
// Add key-value pairs
map.put(1, "Apple");
map.put(2, "Banana");
map.put(null, "Cherry"); // Allows one null key
map.put(3, null); // Allows multiple null values
// Print the HashMap
System.out.println("HashMap: " + map);
}
}
The output of the above code:
HashMap: {null=Cherry, 1=Apple, 2=Banana, 3=null}
Explanation
The example demonstrates the use of a HashMap in Java, which stores key-value pairs. Here's a brief explanation:
1. Creation: A `HashMap` object is created.
2. Adding Entries: Key-value pairs are added using `put()`.
- Key `1` maps to "Apple".
- Key `2` maps to "Banana".
- `null` is used as a key for "Cherry" (HashMap allows one `null` key).
- Key `3` maps to `null` (HashMap allows multiple `null` values).
3. Output: The `HashMap` contents are printed using `System.out.println`.
Key Points:
- HashMap allows one `null` key and multiple `null` values.
- The order of elements in a HashMap is not guaranteed.
Output:
- HashMap: {null=Cherry, 1=Apple, 2=Banana, 3=null}`
Need a detailed understanding of HashMaps?
Have more insights from HashMap IN JAVA – Everything You Need to Know About!
What is a HashTable?
A HashTable is one of Java's classes introduced in JDK 1.0. It also stores data in key-value pairs, similar to HashMap. However, it supports synchronization and is suitable for multi-threaded applications. It is slower in comparison to HashMap and does not allow null keys and null values.
Suppose you are building an online ticket booking system for railways. Thousands of people try to book tickets at the same time. A HashTable can be used in such a scenario where you can map seat numbers to their booking status.
Features of HashTable:
- Thread-safety: it can handle multiple-threaded applications. It has the functionality of synchronization.
- No null keys or values: every key-value pair must be defined and non-null in a HashTable.
Syntax:
HashTable<K, V> table = new HashTable<>();
Where, K = type of keys and V= type of values.
Example:
import java.util.HashTable;
public class HashTableExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a HashTable
HashTable<Integer, String> table = new HashTable<>();
// Add key-value pairs
table.put(1, "Dog");
table.put(2, "Cat");
// Uncommenting these lines will throw NullPointerException
// table.put(null, "Fish");
// table.put(3, null);
// Print the HashTable
System.out.println("HashTable: " + table);
}
}
The output of the above code:
HashTable: {1=Dog, 2=Cat}
Explanation
1. Creation: A HashTable object is created.
2. Adding Entries: Key-value pairs are added using put().
- Key 1 maps to "Dog".
- Key 2 maps to "Cat".
3. Null Handling:
- HashTable does not allow null keys or null values.
- Uncommenting the lines with null will throw a NullPointerException.
- Output: The HashTable contents are printed using System.out.println.
Key Points:
- HashTable does not allow null keys or null values.
- It is synchronized and thread-safe, unlike HashMap.
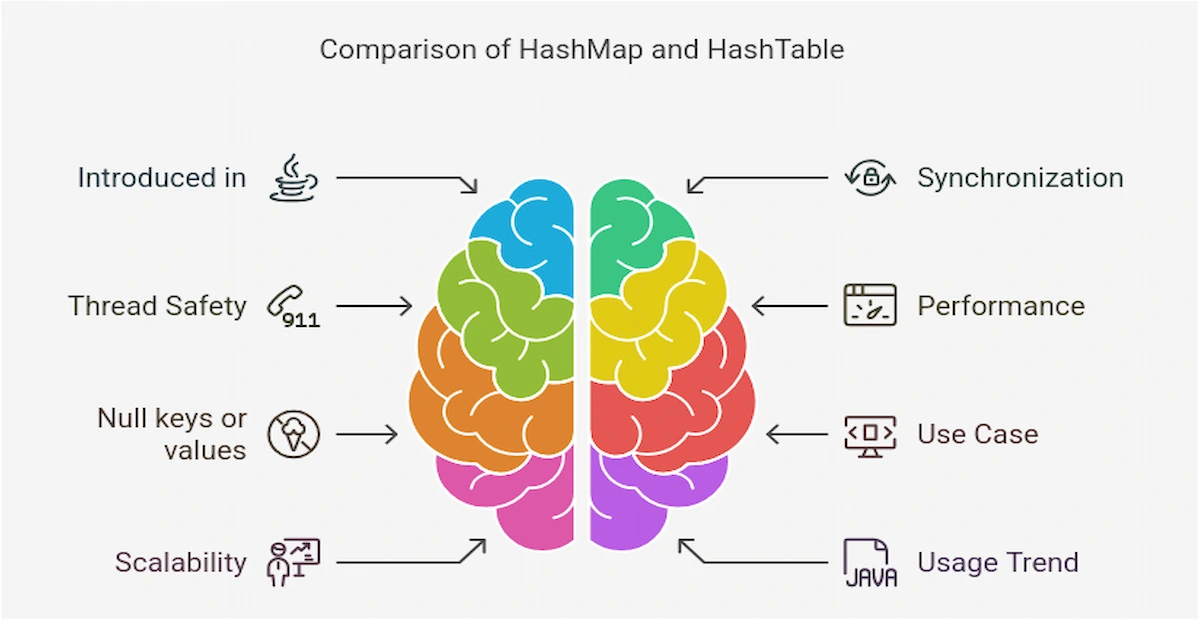
Difference between HashMap and HashTable
HashMap and Hashtable are data structures used to store key-value pairs, but they have some important differences. Here's a comparison between them:
| Features | HashMap | HashTable |
|---|---|---|
| Introduced in | Java 1.2, after Java’s collection framework | Java 1.0, long before establishment of java’s collection framework |
| Synchronization | Not supported | Supported |
| Thread Safety | Not safe | Safe |
| Performance | Faster | Slower due to synchronization |
| Null keys or values | Allows | Does not allow |
| Use Case | Best for single-threaded or externally synchronized applications | Suitable for multi-threaded environments |
| Scalability | Better scalability | Poor scalability |
| Usage Trend | Widely used in modern java applications | Rarely used in modern environments |
If you are new to data structures, you can get help from Data Structures in Java – A Beginners Guide.
When to use HashMap vs HashTable?
In some situations, people often confuse the choice between HashMap and HashTable, as they are data structures that store key-value pairs. Based on the context of your application, you can:
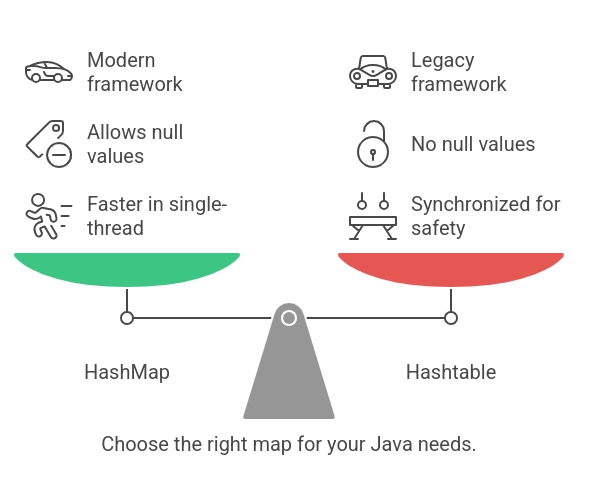
Choose HashMap if:
- You are working on a single-threaded application.
- You do not synchronization
- You need speedy results and faster performance
- You need to store null keys or values
Choose HashTable if:
- Thread safety is your priority
- You do not want to manage external synchronization
- You are in a legacy codebase that already uses it.
Still confused about synchronization and how it works? Don't worry, we have a solution for you: Synchronization in Java!
Best Practices For Modern Java
While the HashTable is suitable to use in a multi-threaded environment and is a safe option for key-value storage in Java, it has been largely replaced by more efficient options like concurrent HashMap.
HashTable synchronizes every process, which means even read operations are blocked if another thread is writing. This reduces the performance of HashTables under high concurrency.
The limitation in HashTable of not allowing null keys or values makes it less convenient than ConcurrentHashMap. HashTable was introduced before the collection framework's establishment; therefore, integrating with new Java libraries and features like streams and lambdas is less flexible and more challenging.
Suggested Read: Collections in Java - Java Collection Framework
HashTable is still available for use but is generally not recommended due to its limitations and inefficiencies. Alternatives like ConcurrentHashMap or wrapping a HashMap are some scalable options in modern world practices. Also, they provide a thread-safe environment with faster performance.
Conclusion
Choosing a data structure is entirely dependent on your requirements. This article has provided in-depth details of HashMaps and HashTables and their differences and usage. In developing modern applications, a HashMap is suitable due to its flexibility and performance, whereas in a multi-threaded environment, a HashTable is preferred. HashTable has some limitations, which are overcome by its alternatives, such as ConcurrentHashMap.
If you are a beginner and want to learn more about Java programming, you can take our free Java course.