- Concept of finance
- Broad areas of finance
- Personal finance
- Business Finance
- Public finance
- Financial management in business
- Goals of Financial Management
- Criticisms on Wealth maximization theory
- Scope of Financial Management
- Functions of Financial Manager
- Financial Instruments
- Financial Markets
- Financial intermediaries
- Key takeaway notes
- Related videos
It is no longer about strategic development. It is about financial management. -Michael Diekmann
Financial management is one of the most sought-after domains in the areas of economics. Especially for those who are aspiring for a career in the area of Banking and Finance, Financial management is a must-learn area.
Well!
Money is something we quickly recall for the discussions of finance or financial management. Of course! We are not wrong. The entire domain of finance revolves around money.
At individual levels, we all know what finance or financial management is. However, with the help of this article or with the help of a financial markets course, let’s try to put our understanding of finance into perspective.
We have a series of concepts to comprehend under the umbrella of financial management, including the concept of finance, the definition of financial management in business, goals of financial management, the scope of financial management, functions of finance manager, the agency theory, Ecosystem of financial system and safety for business investments.
Concept of finance
The term ‘finance’ is derived from economics. We know the basic notion of economics is that the wants are unlimited, but the resources are limited. How an individual, a business, business, or society fulfills unlimited needs using the limited resources available is a fundamental principle of economics.
In the context of business, finance refers to cash, banks, loans, investments, forecasting, borrowing, budgeting, saving, and many other aspects that are directly or indirectly related to money.
Finance is the lifeblood of business without which a business cannot function. Finance plays a critical role from the beginning of a business.
Broad areas of finance
Finance can be discussed under three broad areas as shown below:
Personal finance
As the name suggests, personal finance discusses the sources of income for an individual. For example, an individual would have income from any of the following sources:
- Income from Salary
- Income from house property
- Income from Capital gains
- Income from Business or profession
- Income from other sources
Personal finance discusses these sources in length. Along with the sources of income personal finance also discusses the way an individual spends money that is earned from any of these sources, what is the tax to be paid, what are the investments and the inherent features of each of those investment options available.
When an individual’s expenditure is more than the income, there would be a deficit that an individual would have to fill and he or she may go for loans. Personal finance discusses the institutional framework for lending and borrowing money. The domain also discusses the retirement planning and tax obligations of each individual based on their financial health.
Business Finance
Business finance discusses the sources from which a business can borrow money and how these funds are utilized within the business. Business finance further discusses dividend decisions operating, and marketing decisions taken by the business. The domain also talks about the corporate social responsibility of each business entity. Take up a business finance free course and enhance your knowledge about the concept.
The capital deployed by the businessman to establish the business may often be inadequate to meet the financial needs of the business. Therefore, the businessman needs to hunt for an option to generate funds. Research of the financial requirements and options to satisfy those needs must be done with a definite end goal to arrive at effective financial management to maintain the business.
In a larger business, planning and analyzing the financial requirements are the critical functions of the financial manager since he/she works closely with the top management of the business. Further, the financial decisions are taken at two levels:
- Tactical level: At this stage, the financial transactions of the business are analyzed and the reports are submitted to the financial managers at the next level.
- Strategic level: Data-driven decisions are taken to fulfil the financial requirements of the business.
Further, the finance department of a firm classifies the financial requirements into three categories:
- Short term
- Medium-term
- Long term
However, these sources are leveraged purely based on the business requirements. For example, if the business wants to spend money to pay off suppliers the business focuses on short term funds. While if the business wants to buy long term fixed assets like land and building, furniture and fixtures, plant and machinery, certainly they prefer to raise funds from long term sources since these are the expenditures on long term assets.
Also Read: Scope of MBA Finance in 2022: Top Job Roles, Skills & Opportunities
Public finance
Public finance is about managing the revenues, expenditures, and loans obtained from various sources. A country’s financial health is generally measured through the analysis of the below-mentioned aspects:
- National debt
- Taxation system
- Expenditures
- National budget
- Surplus/Deficit
Public Finance is the way of handling the public funds in the economy of the country, which plays the most significant role in the growth of the nation both nationally as well as globally, and it also touches every stakeholder of the country, whether that stakeholder is a citizen or not.
The revenue of the country is the collection of various taxes and returns on investment, and the government expends from the pool of the revenue. Some of the expenses are medical facilities, healthcare, salaries to the members.
Therefore finance is termed as public finance, where the part of the public is large in terms of influence. It deals with the revenue and spending at every level in which the public is tangled, whether the state level or the central level.
A few critical objectives of public finance are listed below:
- Managing Public basic needs
- The economic prosperity of the country
- Removing income inequality
- Maintaining price stability so that inflation is moderated
Public finance further discusses the demand and supply factors that determine the price. The discussions on foreign trade, gross domestic product, inflation, reserves, and budgeting are some of the important areas of discussion.
Financial management in business
Financial management in business refers to an application of management principles to financial activities in the business. Financial management is the art and science of managing money to meet predefined objectives. It is the process of planning, organizing, controlling, and monitoring financial resources to achieve organizational goals and objectives. In business, financial management is the process of handling a company’s finances in a way that generates value for the overall business. Financial management is an organic function in business undertaken by some dedicated departments and designated managers.
In a nutshell, financial management is about the following:
- Actions to reduce the cost of finance
- Confirms sufficient availability of funds
- Deals with the planning, organizing, and controlling of financial activities like the obtaining and utilization of funds for various financial needs within the business.
Also Read: Best Business Finance Books every young entrepreneur must-read
Goals of Financial Management
The goals of financial management can be grouped in many ways. However, most of those goals are overlapping and ultimately boils down to the following three goals.
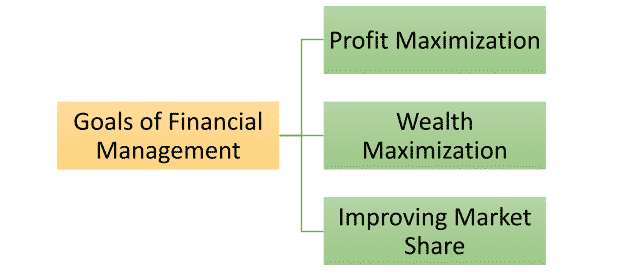
Profit maximization
Profit is one of the most traditional yet popular goals of financial management. In economic terms, profit refers to an excess of revenues over the cost. Profit is considered as the fuel for a business which keeps the engine of a business active all the time.
The term profit is subject to interpretation. There are different classes of profits we can observe in a business. For example,
- Profit before Tax (PBT)
- Profit after Tax (PAT)
- Earnings before Interest and Taxes (EBIT)
- Earnings before Tax Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA) and many more of that categories.
Arguments in favour of profit maximization theory
Well, there are certain arguments in favour of the profit maximization theory.
The basic purpose of business is to earn profit. No business begins and runs for charity. Of course, if there is a charitable intention then the business ceases to exist and becomes a charitable institution. A business begins and runs for profit. Profit is the motive behind every business. Often profit is considered as the meter for success. The business that earns profit can manage itself without developing dependency promoters or the government. Only profit-making entities can think of tomorrow and beyond and those business entities struck in losses would become a burden to the society at large. Another important aspect to understand is that the term profit is accepted in many societies as long as it is earned in legitimate ways.
The profit is critical for a business to pay off their employees salaries, pay suppliers, pay all outstanding financial obligations. A loss-making company would have to depend on external sources of funds to take care of financial responsibilities, while a profit-making business generates funds within the business.
There are many ways in which a business can improve its profit.
For example, increasing units sold, increasing the price and cost minimization. Business entities choose to look out for new business opportunities, acquire businesses, and expand into different industries to capitalize on the potential and promising business opportunities.
Well!
There is a dark side to the story
The theory of profit maximization has been criticized by many scholars. Many of these criticisms are valid under various considerations. Some of the important aspects are discussed in detail below:
The concept of profit is not clear
Scholars expressed that the concept of profit is not clearly defined. The business needs to define whether it is gross profit, net profit, profit before tax, profit after tax, earnings before interest and tax, earnings after tax, profit before interest, tax, depreciation and amortization.
Duration
The duration in which the business is required to earn this profit is unclear. Many business firms sacrifice their long term profits by overemphasizing the short term gains which hurt the business in the long term. The business should consider itself as a going concern by a focus on creating long term value for all the stakeholders involved in the business.
Scale
Many times business firms ignore the synchronization between the size of the business and volume and frequency of profit. For example, a business started with a capital of Rs 10,000 generating Rs 10 lakhs creates suspicions around the business since it is an abnormal profit for a business considering the benchmark in the industry.
Consideration of time factor
The profit maximization theory considered ignore the concept of the time value of money which is one of the building blocks of financial management. The value of money changes(mostly declines) over some time. If the time factor is ignored, no matter what profit is generated makes no sense to the business. For example, earning an insignificant amount of profit by spending substantial time in the business. Further, this theory ignores the risks associated with the profit.
Social evils
Undue aggression towards profit maximization may lead to social evils like Corruption, quality drop, wrong selling, false promises, and undue influence.
Wealth Maximisation
The second most popular goal of financial management is to increase the wealth of business. This is the most modern approach towards the goals of financial management. This is also called value maximization since this theory focuses on increasing the value of the business to increase the value of shares by creating wealth for the stakeholders. When we say stakeholders, there are two important categories of stakeholders we can see in any business.
Internal stakeholders and external stakeholders as shown below:
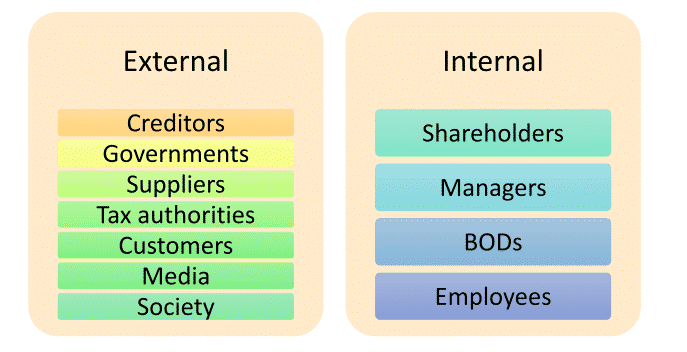
The term wealth is explained under two parameters. Wealth maximization in business mostly refers to improving the market price of the share and enabling the business to pay frequent dividends so that the investors are motivated enough to continue in the business.
In simple terms, wealth in business refers to NPV= Present value of the benefits-Present value of costs.
The wealth maximization theory takes care of the larger interest of the stakeholders. The wealth in this context is based on cash flows and not on profits. This theory emphasizes long term perspectives rather unlike profit maximization goal focusing on the short term.
It is very important to note that the wealth maximization analogy appreciates time factor, risk factors and uncertainty factors in the business; this helps board members of the business to create strategies that enhance the long term value for the stakeholders.
Criticisms on Wealth maximization theory
Wealth maximization theory is not free from criticisms. The theory is criticized under the following grounds:
It is a prescriptive idea, not a descriptive one
Wealth maximization theory is prescriptive and not descriptive. Though it is accepted that wealth maximization is required, there is no interpretation of how to create this wealth within the business to add long term value for the stakeholders.
Not socially desirable
When wealth maximization becomes the goal of financial management, there is scope for business entities engaging in accumulating wealth that otherwise belongs to all the industries within the economy.
For example, accumulation of wealth only in the few hands like Jeff Bezos, Elan Musk, Mark Zuckerberg, Ambani, Alibaba, Bill gates would result in the entire country’s wealth being accumulated by a few individuals which are not socially desirable. Though the contribution of these individuals towards industry, country and society at large, the accumulation of wealth to that large extent would introduce many other seriously. For example, only a few players in the telecom industry would create the problems listed below:
- Higher prices
- Lower competition
- Unavailability of alternatives
- Fear of acquisitions and takeovers
Maximizing stakeholder’s value is unclear
The theory states that wealth maximization is critical for the survival of the business. However, the theory does not clearly state the specific set of stakeholders whose value is increased.
The question arises how wealth maximization theory enhances the value of a certain specific set of stakeholders like debenture holders, bondholders, creditors and other investors who deploy their financial resources for a fixed rate of interest. Because no matter what profit or wealth is created within the business, debenture holders are paid only the fixed rate of interest irrespective of whether a business is under profit or deep losses.
Also Read: Applications of Data Science in Finance
Exploitation
In an urge to create wealth, a business may indulge in social evils like corruption, fabricated prices, overtime work for employees etc. Further, when a wealthy entrepreneur acquires all major players in the industry, they may start exploiting customers and consumers in terms of higher prices on products and services
- Quality drop
- Compromise on after-sale services
- Less attention to environmental pollution
- Insensitive towards the harm that the product would indirectly create to the consumers etc.
Improving market share
The business entities may start with a humble beginning but they dream to acquire market share. Market share gives a general idea of the size of a company about its market and its competitors. The market leader in an industry is the company with the largest market share. The calculation for market share is usually done for specific countries or regions.
For example, In Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) HUL is leading the industry with the highest market share followed by ITC and Britannia. Similarly, in the telecom industry, Jio has the largest market share followed by Airtel, Vodafone. In the automobile industry, Maruti Suzuki has the largest market share followed by Hyundai, Tata, M&M, and Honda.
The investors or the individuals who are interested in a business can access the market share details from various sources. For example,
- Published annual reports
- Television
- Newspapers
- Magazines
- Podcasts
- Social media etc.
It is important to note that when the business improves the market share, it can start enjoying economies of scale, reducing the competition resulting in the growth of revenues. A few important means to improve market share are listed below:
- Reducing cost
- Increase volume of sales
- Promotion
- Improving efficiency
- Introducing new products
- Customization and standardization
- Customer loyalty
- New technologies
- Talent retention
- Acquisitions
Nevertheless, the market improvement goal of financial management has also been criticized by several scholars. When the main goal of financial management is towards improving market share in an inconsistent manner that may lead to a monopoly where single-player rules the entire market leaving no scope for customers to choose between. Market share improvement may also lead to a duopoly where only two players rule the entire market by fixing the price that they are pleased with. When there are fewer alternatives, high prices, and unethical practices, the business would be off track from the mainstream of business where the business is expected to earn profit through legitimate routes.
Scope of Financial Management
There are three important areas in which we can discuss the domain of financial management. Though several factors are discussed under financial management ultimately most of those aspects boils down to three important areas as shown in the following picture.
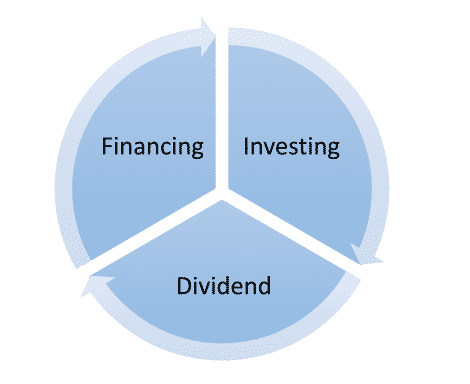
Let us understand each of these areas in details:
Financing Decisions
A financial manager is required to take decisions on the sources of finance available to be chosen for obtaining funds. Please note selection of the right source for financing is a critical decision since it will have a domino effect on business. For example, when the business is looking for expand operations to different geographical locations and the business is expected to take some time to break even, then it Is not a feasible idea to go for short term sources of financing. Similarly, when the business needs funds to take care of the working capital deficit, it is a wise decision to go for sources of finance that are short term in nature. For example, loans from commercial banks, trade credit, overdraft facilities etc. instead of going too long term sources.
Further choosing the right mix of various sources of capital in the capital structure is a critical decision of a finance manager since it will have an impact on the overall business.
Investing Decisions
Investing decisions are equally critical in a business. When the finance manager brings funds to the business, it is important to make use of those resources in such a way that creates value for the business in the long run. Also, the choice of investments in various projects needs to be carefully decided. That is the reason the role of the finance manager is critical in capital budgeting decisions.
A business should pick where to invest in order to gain the uppermost imaginable returns. This decision narrates the cautious selection of assets in which funds will be invested by the firms. The firm puts its funds in obtaining fixed assets and current assets. When choice with respect to a fixed asset is taken it is known as a capital budgeting decision.
A bad capital budgeting decision usually can relentlessly harm the financial wealth of a business. A bad working capital decision affects the liquidity and profitability of a business.
Dividend Decisions
The financial decision narrates the payout of profits back to investors who provided capital to the firm. The word dividend refers to that part of the profits of a company that is circulated by it among its shareholders.
It is an incentive of shareholders for investments made by them in the share capital of the company. The dividend decision is related to the quantum of profits to be dispersed among shareholders.
A decision has to be taken whether all the profits are to be shared, or maintain all the profits in business or to keep a portion of profits in the business and distribute others among shareholders. The higher rate of dividend might raise the market price of shares and thus, maximize the wealth of shareholders. The firm should also reflect the question of dividend constancy, stock dividend, and cash dividend.
To pay or not to pay a dividend to the shareholders is one of the most critical decisions to be taken in the area of management. This is a double-edged sword that hurts either way if not handled properly.
Generally, companies prefer to pay a dividend at scheduled intervals as and when the business earns a profit. For example, companies pay a dividend once a year, considering the level of profit. When a business pays a dividend, it motivates the investors since the very reason many investors take shares is to earn a dividend. When the dividend is distributed, the investors may have faith and positive beliefs about the performance of the company. These positive vibes improve the visibility of the company in the industry.
On the other hand, some companies do not prefer to pay frequent dividends; instead, they prefer to make use of the profit by investing in profitable and potential business opportunities, thereby improving the value of shares. This is also called Capital gain. However, when a company does not pay a dividend, the investors may get discouraged since there are no short-term gains by investing in a stock.
However, striking the right balance between paying or not paying a dividend is a critical decision for a finance manager.
Functions of Financial Manager
Well! After understanding the scope of financial management, it is important to continue understanding the functions of a financial manager since it is interconnected. Some of the most common functions performed by a financial manager are briefly discussed below:
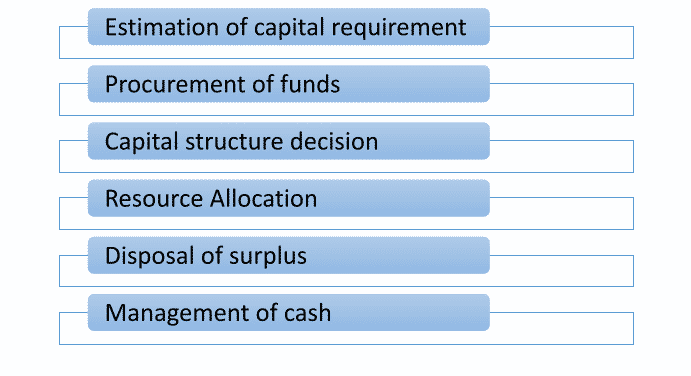
Estimation of capital requirement
A finance manager has to make an approximation about the capital requirements of the company. This will depend upon expected expenditures, expenses for future projects. The capital estimation is done two ways
- Funds required to buy long term assets, maintain long term assets and expand business
- Funds required to take care of working capital requirements
Procurement of funds
Once the requirement capital estimation is done, now it's time to find out the right source of funds from the market. There are a series of options available out of which finance needs to handpick the source of funds considering the cost and benefits. Finance managers need to analyses each of the options available carefully to understand inherent limitation of each source of capital.
Capital structure decision
Creating the right mix of sources in the capital structure is critical for a business. Once the requirement of capital funds is finalized, a decision with regards to the kind and proportion of various sources of funds has to be taken. For this, the financial manager needs an adequate mix of equity and debt and short-term and long-term debt proportion. This is done to accomplish the minimum cost of capital and maximize shareholders wealth.
Resource Allocation
Once the funds are acquired, the manager must allocate funds appropriately within the organization and ensure the funds are effectively utilized to create long term value for the business.
Nevertheless, there are three guiding principles for the allocation of funds within the organization.
- Safety
- Liquidity
- Profitability
Disposal of surplus
The financial manager should decide on how much to preserve for reinvesting and how much to distribute as dividends to shareholders out of the profits of the company. The factors which impact these decisions include the trend of earnings of the company, the trend of the market price of its shares, the necessities of funds for self-financing the future projects and so on.
Management of cash
Management of cash and other liquid assets is an imperative task of a financial manager. It encompasses projecting the cash inflows and outflows to confirm that there is neither shortage nor surplus of cash with the organisation. Adequate funds must be accessible for the acquisition of materials, payment of salaries, wages and meeting day-to-day expenses.
Agency theory
Agency theory is also referred to as agency problem or agency dilemma. Agency theory is an idea used to elucidate the central associations between principal and their relative agent. In the fundamental sense, the principal is somebody who profoundly depends on an agent to execute specific financial decisions and transactions that can result in changeable outcomes. Since the principal depends so profoundly on the agent to make the accurate decision, there may be a variety of conflicts or differences—Agency theory bars into such relationships.
In simple terms, agency theory is a fiduciary and consensual relationship between two or more parties in which parties involved will have their own set of duties and responsibilities. In a business, shareholders are the principal, and the Board of directors is the agent. Since shareholders cannot participate in the day-to-day affairs of the business and do not have the requisite skills to manage the business, they hire individuals or groups of individuals to take care of the business in the best interest of shareholders. This way, the ownership and control are differentiated in the business for better management of the business.
When agents are unable to take care of the best interest of the shareholders, that's when the agency problem arises.
To regulate whether or not an agent acts in the best interest of their principal, the standard of "agency loss" has developed as a normally used metric. Exactingly defined, agency loss is the variance between the ideal results for the principal and the significance of the agent's behaviour. For instance, when an agent regularly performs with the principal's best interest in mind, agency loss is zero. But the further an agent's engagements deviate from the principal's best interests, the greater the agency loss becomes.
Financial System
The financial system is a broader system that encompasses all the borrowers, financial institutions, and lenders within the economy. The financial system also comprises sets of rules and practices that borrowers and lenders use to decide which projects get financed, who finances projects, and terms of financial deals. The financial system of any country can be broadly discussed under three important categories as shown below:
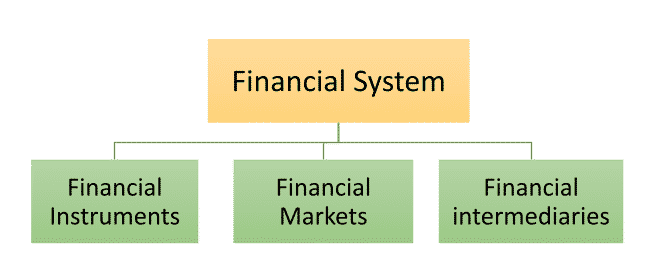
Let us understand each of these categories in detail:
Financial Instruments
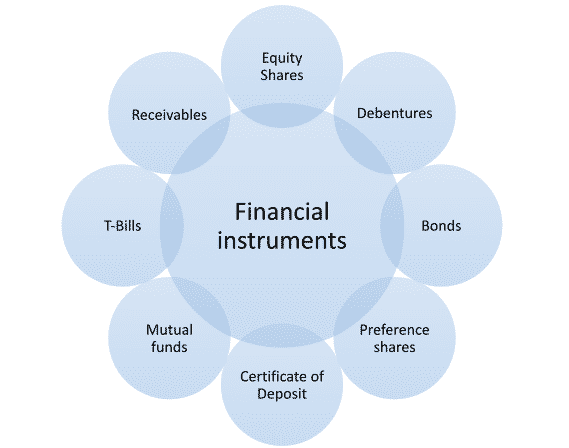
A financial instrument is a real or virtual document representative of a legal agreement involving any kind of monetary value. Financial instruments can be real or virtual documents representing a legal agreement involving any kind of monetary value. Equity-based financial instruments signify ownership of an asset. Debt-based financial instruments signify a loan made by an investor to the owner of the asset.
In simple terms, the financial instrument is an asset that has some economic value eligible for trading in the market. The financial instruments can be long term or short term or real or virtual. Some of the most important financial instruments are shown in the following diagram.
Further, financial instruments can be classified into two broad categories:
- Money market instruments
- Capital market instruments
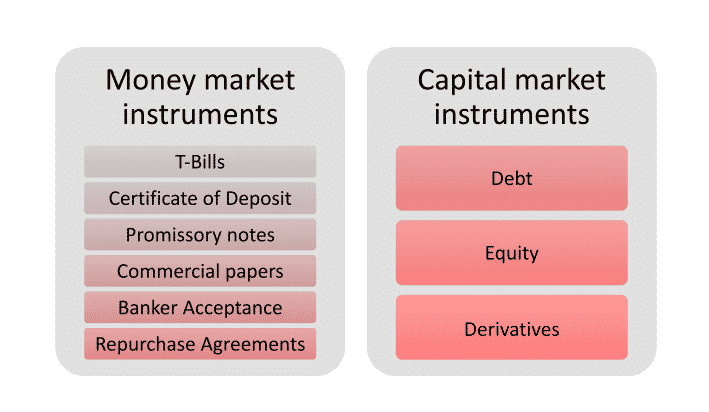
The money market mentions trading in very short-term debt investments. At the wholesale level, it comprises large-volume trades between organizations. At the retail level, it comprises money market mutual funds bought by individual investors and money market accounts opened by bank customers.
There is a range of instruments traded in the money market in both the stock exchanges, NSE and BSE. These include T-bills, certificates of deposit, commercial paper, repurchase agreements, etc. Subsequently, the securities being traded are extremely liquid, the money market is considered a safe place for investment.
A capital market is a market for medium and long term funds. It comprises all organisations, institutions and instruments that offer long term and medium-term funds. It does not include the institutions which provide finance for less than one year. The common instruments used in capital markets are shares, bonds, debentures, bonds, mutual funds etc.
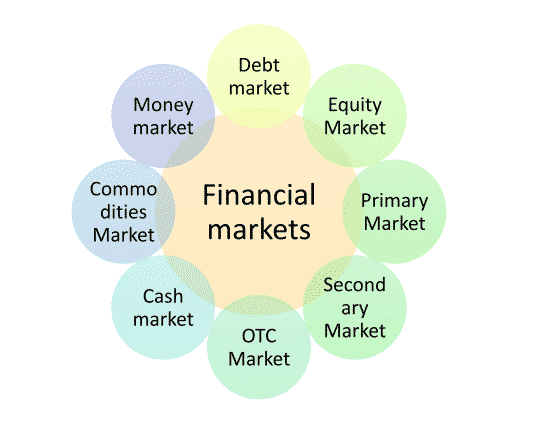
Financial Markets
Financial markets refer generally to any marketplace where the trading of securities occurs. There are different kinds of financial markets, including forex, stock, and bond markets. These markets might include securities that are either listed on regulated exchanges or else trade over-the-counter (OTC). Financial markets trade in all kinds of securities and are important for the smooth operation of a capitalist society. When financial markets fail, financial disruption including recession and job loss can result.
The term market is every so often used for what are more strictly exchanges, business firms that facilitate the trade in financial securities, for example, a stock exchange or commodity exchange. This may be a physical location or electronic system.
Financial markets play a dynamic role in easing the smooth operation of capitalist economies by assigning resources and generating liquidity for businesses and entrepreneurs. The markets make it easy for buyers and sellers to trade their financial holdings. Financial markets produce securities products that provide a return for those who have excess funds and make these funds available to those who require money.
Some of the most important financial markets are shown in the image below:
Financial intermediaries
Financial intermediaries are the people, institutions or business firms that connect buyers and sellers in the markets. They facilitate trading activities by offering a platform for the exchange of financial products. The intermediary could be a bank, insurance company, mutual fund, brokers, sub-brokers, stock exchanges etc.
Financial intermediaries deliver a middle ground between two parties in any financial transaction. A prime instance would be a bank, which helps many different roles: it acts as a middleman between a borrower and a lender, and pools together funds for investment. Some of the most important financial intermediaries are shown below:
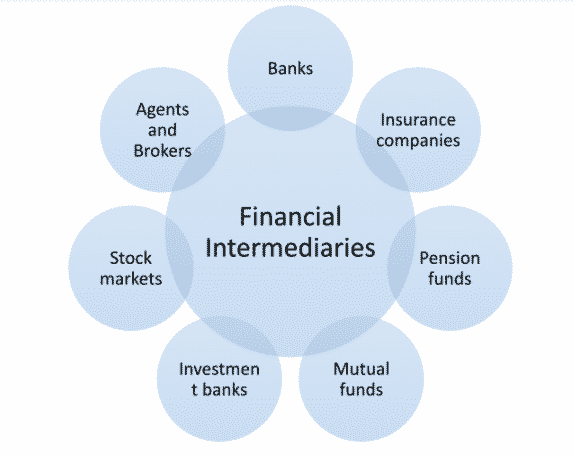
Brokers help investors in buying and selling stocks in the stock market, banks connect those who are in need for money and those who are in excess of money, insurance companies connect individuals and business organizations with the insurance products, mutual funds collect funds from pool of investors and invest on various financial instruments. Nevertheless their role as a financial intermediary is very critical since they are the connecting hub in the entire financial system. These intermediaries help create efficient markets and lesser the cost of doing business.
Key takeaway notes
Here is a quick recap of what we have learned so far:
- Finance is all about money. It talks about cash, banks, investment, saving, forecasting, borrowing, investing, and budgeting.
- Broad areas of finance: Personal finance, Business Finance and Public finance.
- Financial management is the art and science of managing money to meet predefined objectives.
- Goals of financial management: Profit, Wealth and improving market share.
- Stakeholders to the business: Internal & External.
- Financial management encompasses investing, financing and dividend decisions.
- The principal-agent relationship is an arrangement where one entity lawfully selects another person to act on its behalf.
- Financial instruments, financial markets and financial intermediaries are the constituents of the financial system.
If you are looking to upskill yourself in the Management domain, check out the Best Management Courses and elevate your learning journey to the next level!
Related videos
Time Value of Money | Concept of Time Value of Money | Great Learning
Introduction to Corporate Finance | Corporate Finance Tutorial | Great Learning
Introduction to Financial Management | Function of Financial Management | Great Learning