If you are looking for a career in product management, you are in the right place. Recently, the role of product management has been expanding significantly and gaining traction. The online interest in this role has doubled in the last five years. This is majorly due to the growing importance of data while decision-making and increased focus on the audience/customer and the design. The evolution of software development methodologies has also fueled this growth.
Is this the proper role for you? Yes, if you love understanding who your customer is, why they behave the way they do, and their needs. If all of these tick your boxes, then yes, product management is your proper role. Take a Product Management Course and gain skills such as Product Life Cycle, Product Management Strategy, Product Leadership, and Product Innovation.
But what does a product management job involve? What are the responsibilities or skills required? And so on. We will answer all these questions as you read ahead.
What is product management?
As Martin Eriksson famously said, Product management is the intersection of technology, business, and user experience.
- Technology: To know what is being built, it is crucial to understand how it is being built. This does not mean the product manager has to sit down and code. Product managers must have a fair idea about the technologies involved and the amount of work put into making the product. Only then will they be able to make the right decisions in the development strategies.
- Business: The ultimate aim of product management is to boost business. Product managers must be obsessed with optimizing the product to better cater to the customers, directly affecting sales and return on investment.
- User Experience: Building better products can only be possible if the customers and their feedback are heard. In this scenario, the product managers are the customers’ voices inside the business and must communicate what the customers desire to help improve products effectively.
The need for product management emerged when companies needed exclusive help with their product lifecycle. There was a need for functionality to support the development and pricing and to understand the customer and the product first. Product management helped achieve these requirements. It became an organizational function to build the best possible products and help understand the customer better.
As the focus shifted to understanding the customers, product teams could now build better products. Companies realized that this directly boosted their product sales, and thus product management became a critical organizational function.
Check out Great Learning Academy’s Free Product Management Course to learn more about Product Management.
Product Manager Job Description
The Product Manager is responsible for end-to-end product life-cycle management, including product planning and product marketing basis customer requirements. A few of the essential responsibilities of a product manager include defining the product vision, setting up overall strategy and goals, managing revenue, and working with sales, marketing, and engineering teams. Check out the product strategy course to enhance your knowledge of how to develop a product successfully. Given below is the detailed job description with the roles and responsibilities of a product manager:
- Defining product strategy and roadmap
- Conducting detailed primary and secondary market research
- Collaborating with various teams such as sales, marketing, design(UI/UX), and engineering
- Developing product vision and core positioning for the product
- Performing competitor analysis
- Curating monthly reports
- Managing revenues and working on pricing of the product
- Working on partnership and licensing opportunities with internal and external stakeholders
- Performing product demos
- Leading and managing team members
- Training team members on important product management aspects to ensure success
- Collecting, analyzing data, and forecasting key observations
- Developing a business strategy and handling recruitment
- Staying on top of consumer demands and market trends
Product Manager Responsibilities
A product manager‘s major responsibilities entail making strategies and tactical planning. To break it down, we have listed some of the significant responsibilities:
Conduction of Research: Product managers spend most of their time doing research. This research can vary on a wide range of requirements. They predominantly research their product, its uses, its scope, and the market for it. Furthermore, they research the product’s user persona and try to gain expertise in building a user-feedback-oriented, better-designed product. Also, they are required to research their competitors and understand the competitor’s products. This helps them strategize in making their products different and better. It also helps them price their products better and learn from their mistakes.
Strategy Development: This is the next important responsibility of a product manager. Gaining insights after extensive research can only be fruitful if that research is utilized best. Product management requires you to build strategies for the company’s products based on industry research. This can be a vision and a roadmap for the product and its development lifecycle. Making strategies also include designing goals and objectives, so that product development is on track.
Communicating Plans: Communication is the key, even in product management. Each of the former responsibilities fails to be appropriately executed if a product manager fails to communicate. A product manager has to communicate in two directions: the key stakeholders and the relevant teams who work on the product. The key stakeholders must communicate the research insights and the strategies to be executed. The product teams, development teams, etc., must be communicated about the requirements and the roadmap/plan to execute the development process and the strategy efficiently.
Coordination between/in teams: A product manager has to be steady in coordinating with the teams once the development cycle begins. They must identify the various pitfalls/issues in the product development process and help rectify them. This will help the teams to achieve their goals as per the roadmap.
Feedback data analysis: After successfully building the product and launching it into the marketplace, a product manager must effectively collect customer feedback. They must collect and analyze the feedback to determine what changes could be made to the product to better cater to the customer’s needs. They must understand what’s working and what is not, and they can incorporate these changes into future product versions.
The responsibilities mentioned above can also be entailed as the steps of the Product Management Process. This also sheds some light on what kind of skills you would be required to pursue a career in product management. However, there are some other additional skills that a product manager is required to have.
The ideal job for any individual in product management would be that of a product manager. The product manager is someone who manages one or multiple products across the same or various departments.
Example: Product Manager working on a UX (user experience) of an android application.
However, the responsibilities of a product manager will vary depending on the type of product, business goals and the organization.
The product manager is like the captain of the IPL team but not the owner who is majorly responsible for the franchise’s overall success (business/product). They conduct research, strategize, and shape the vision considering the end-users and all stakeholders.
Now, let us dive into detail to know more about various product management job roles.
Product Management Career Path
This is how a typical Product Manager’s Career Path looks like:
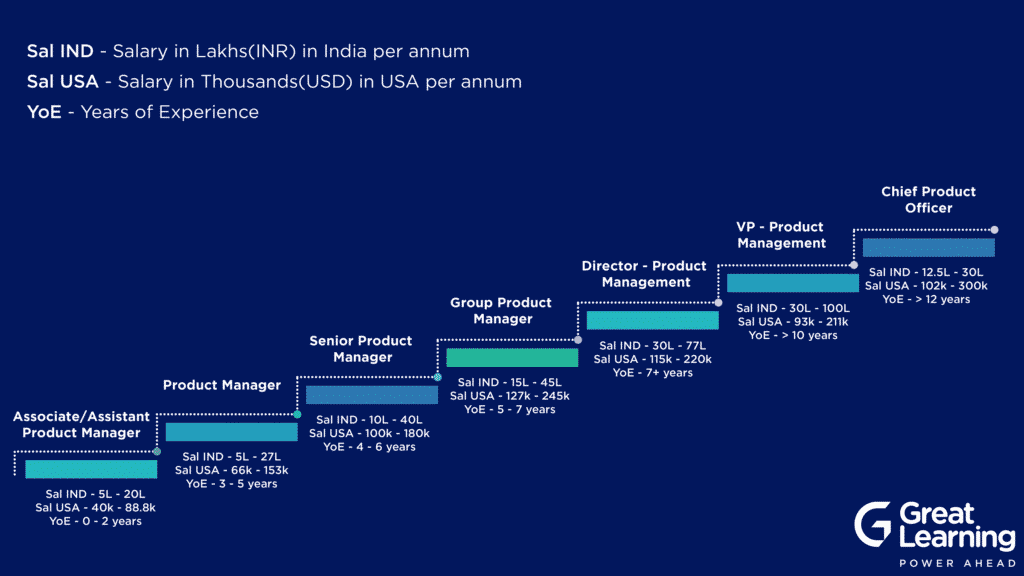
1. Assistant/Associate Product Manager (APM)
Assistant/Associate Product Managers generally report to Product Managers, and their responsibilities are similar to Product Managers but on a smaller scale. APM is typically an entry-level role and requires a willingness to adapt, change and learn depending on the consumer requirements. There are a lot of learning opportunities for young professionals in this role as they directly work with the Product Manager and can learn from them on team management and decision making.
Responsibilities:
- Conducting market research
- Data analysis
- Coordinating with multiple stakeholders
- Working on developing new product strategies and roadmap
- Preparing project reports and tracking the project
- Working on UI/UX with the design/software team
2. Product Manager (PM)
Product Manager is generally a mid-level role, and prior experience in product management is mandatory in most cases. Here they own the product and might work across various departments/teams. In most organizations, PMs will be the go-to person for anything needed on the product and will work closely with sales, marketing, design and other teams. PMs must know their competitors well and be aware of everything happening in the product space.
Responsibilities:
- Defining product strategy and roadmap
- Developing core positioning and vision for the product
- Coordinating with multiple teams
- Performing product demos
- Managing teams and internal/external stakeholders
- Thorough understanding of competitors
3. Senior Product Manager (SPM)
Senior Product Managers generally coordinate with senior heads of different teams such as sales, marketing, design, and others. They work closely with a leadership role and clientele. They are responsible for overall team management, including product managers, engineering managers, analysts, associate product managers, and the entire product team. SPMs are also responsible for budgeting and promotion of the product. This role generally requires at least five years of experience in the product management space.
Responsibilities:
- Developing product strategy and roadmap
- Developing a business strategy and managing budgets
- Building robust processes for an effective end-to-end product lifecycle
- Coordinating with senior heads of various teams
- Managing internal/external stakeholders
- Thorough understanding of competitors
- Managing a large team
- Analyzing and reporting big data
- Handling recruitment
4. Group Product Manager(GPM)
Group Product Managers are product leaders who have more interactions with executives. They need to stay constantly updated with new trends and things happening in the market related to the product space. They are problem solvers known for anticipating, identifying and managing risks. Negotiating with external stakeholders for various collaborations will be one of their key responsibilities. They will have to oversee the entire team from junior to senior levels and manage conflicts as they arise (if any).
Responsibilities:
- Developing a business strategy and managing budgets
- Build robust processes for an effective end-to-end product lifecycle
- Coordinating with senior heads of various teams
- Negotiating with external stakeholders
- Risk analysis and mitigation
- Managing a large team
- Handling recruitment
5. Director – Product Management
The Director of Product is a leadership role generally responsible for overall product planning and execution and will require less hands-on involvement in indirect product management. The part involves making critical decisions around product strategy, vision and marketing/outreach. They collaborate with directors of other departments such as manufacturing, operations, sales, marketing and finance to ensure everything is in place.
Responsibilities:
- Developing a business strategy and managing budgets
- Coordinating with senior directors and leaders of various teams
- Negotiating deals and collaborations
- Risk analysis and mitigation
- Build scalable business via product marketing and outreach
- Stay on top of consumer trends and market demands
6. VP – Product Management
The Vice President of Product Management is also a leadership role that focuses on managing teams and product lines. The hands-on involvement decreases with Product Managers working to build teams, optimise processes and stay up-to-date on what is happening in the product space. They are the company’s face in media, events and conferences and play a key role in strategic decisions. Acting as a bridge between the product team and CXOs plays a crucial role in the business.
Responsibilities:
- Owning product vision and route map
- Coordinating with C-suite level leaders and product team
- Building scalable business via product marketing and outreach
- Staying on top of consumer trends and market demands
- Interacting/meeting with consumers
- Identifying and building partnerships
7. Chief Product Officer (CPO)
CPO is a C-level executive in charge of the big-picture product strategy and plays a significant role in long-term goal setting. This role is typically in large organizations such as MNCs and Fortune 500 companies. CPO’s responsibilities begin with product research and extend beyond the product’s release. The CPO reports to the CEO and closely works with all critical C-level stakeholders.
Responsibilities:
- Responsible for long-term vision and goal setting
- Coordinating with C-suite level leaders and product team
- Product growth and Marketing
- Building a structured product organization
- Interacting/meeting with consumers
- Identifying and building partnerships
- Interviewing and recruiting team members
- Managing budgets, revenue and profit share
A day in the life of a product manager
You must now be curious about how your day will go at work if you become a product manager. Let us dive into a discussion about the tasks that describe a day in the life of a product manager.
Based on research and interactions, a product manager’s job can be divided into five categories:
- Customer Feedback and Interaction
- Managing Product Development
- Communicating/Connecting with Team members
- Research, Planning, and Strategy
- Documenting/Reporting
Here are examples of tasks that fall in each category:
1. Customer Feedback and Interaction
- Interacting with Customers on key issues/problems
- Solving customer problems
- Hearing pain points and understanding customer needs
- Taking feedback from customers and taking actionable steps accordingly
2. Managing Product Development
- Ideating and performing Idea analysis
- Evaluating product concept
- Setting up processes as a part of product development
- Tracking the progress
- Making Product Improvements
3. Communicating with Team members
- Hosting regular team meetings
- Meeting with senior management/leadership team to understand industry trends/updates and competitive market
- Regular meetings with the development team to check progress and review demos
- Regular meetings with sales team to ensure they have proper product knowledge and updates and conducting training sessions accordingly
- Meeting regularly with design and engineering team to discuss technical aspects basis customer requirements
- Meeting with the marketing team to check on campaigns, social media launch, and overall marketing strategy
4. Research, Planning, and Strategy
- Performing Competitor Research
- Reviewing Product Sales and Marketing Numbers
- Managing Revenue
- Pricing Analysis
- Review other KPIs – Key Performance Indicators
- Creating decks related to the product for Sales teams
- Creating Product Marketing Strategy
- Analyzing data and creating reports with forecasts/predictions
- Reviewing customer feedback, new features, and functionalities
5. Documenting/Reporting
- Creating MoM(Minutes of Meeting) and documenting key takeaways from all meetings
- Ensuring data points reach the right stakeholders for analysis and further improvements
- Creating weekly/monthly reports with forecasts/predictions to stay on top of the project
Product Management Salaries in USA and India
You must be interested in knowing how much a product manager earns. Here is an overview of salaries of various product management roles in India and USA:
Product Manager Salary: Based on Experience/Job Roles
| Job Role/Careers | Salary in USA in USD | Salary in India in INR |
| Assistant/Associate Product Manager | 40,000 – 88,800 | 5,00,000 – 20,00,000 |
| Product Manager | 66,500 – 1,53,000 | 5,00,000 – 27,00,000 |
| Senior Product Manager | 1,00,000 – 1,80,000 | 10,00,000 – 40,00,000 |
| Group Product Manager | 1,27,000 – 2,45,000 | 15,00,000 – 45,00,000 |
| Director – Product Management | 1,15,000 – 2,20,000 | 30,00,000 – 77,00,000 |
| VP – Product Management | 92,900 – 2,11,000 | 30,00,000 – 1,00,00,000 |
| Chief Product Officer | 1,02,000 – 3,00,000 | 30,00,000 – 1,00,00,000 |
Sources: LinkedIn Salary for USA and Glassdoor for India
Product Manager Salary: Based on Company
| Company | Salary range in USA in USD per annum |
| 137,000 – 214,000 | |
| Amazon | 77,200 – 148,000 |
| Meta (previously Facebook) | 130,000 – 227,000 |
| Cisco | 103,000 – 168,000 |
| Microsoft | 110,000 – 159,000 |
| Apple | 105,000 – 182,000 |
| Citi | 82,700 – 151,000 |
| Company | Salary range in India in INR per annum |
| ICICI Bank | 3,60,000 – 16,32,000 |
| Axis Bank | 4,80,000 – 14,00,000 |
| TCS | 5,51,000 – 34,40,000 |
| Microsoft | 17,00,000 – 33,80,000 |
| Paytm | 6,48,000 – 46,40,000 |
Sources: LinkedIn Salary
Product Management Salary: Based on Skills
| Skill | Average Salary in India in INR |
| Product Management | 13,27,401 |
| Product Development | 14,03,854 |
| Product Marketing | 11,66,528 |
| Strategic Planning | 12,12,891 |
| Project Management | 12,28,645 |
Product Management Skills
Product Managers come from diverse backgrounds ranging from Engineering to Sales and marketing. Different skill sets are required, but one can build on their strengths and improve in other areas. The skill sets might vary depending on the role and the product. Here are a few general critical skills required to be a product manager:
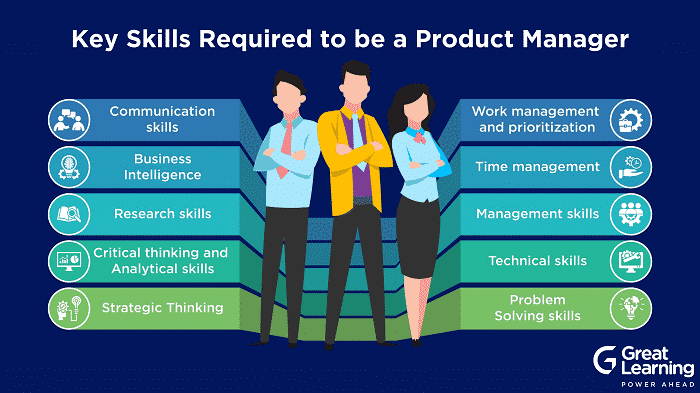
- Communication skills
- Business Intelligence
- Research skills
- Critical thinking and Analytical skills
- Strategic Thinking
- Work management and prioritization
- Time management
- Management skills
- Technical skills
- Problem-Solving skills
Storytelling: Due to their extensive research on customer persona, Product managers learn more about their customers than the sales team. Storytelling skills will help them better explain to their customer to the rest of the company.
Marketing: This skill will help product managers integrate the language of their customers/buyers into messaging of their company’s product. Understanding basic marketing concepts will help product managers help design and provide products people can find and relate to.
Empathy: This is one of the most essential skills required by a product manager. They should have empathy for the developers for how they work. They should have empathy for the upper management for their schedules and, most importantly, empathy for the end-users/ customers for their needs and pain points. This will help the product manager to coordinate effectively and function well.
These product management skills are actively marketed by professional development boot camps, universities all over the world, proving that product management is here to stay.
Conclusion
Product management is different for different companies, and this is because their products, their way of functioning, and their organizational structure are different. But, the aim of Product management remains the same throughout every company – to boost product sales and, ultimately, the business.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does a project manager do?
The Product manager generally executes all the product management principles.
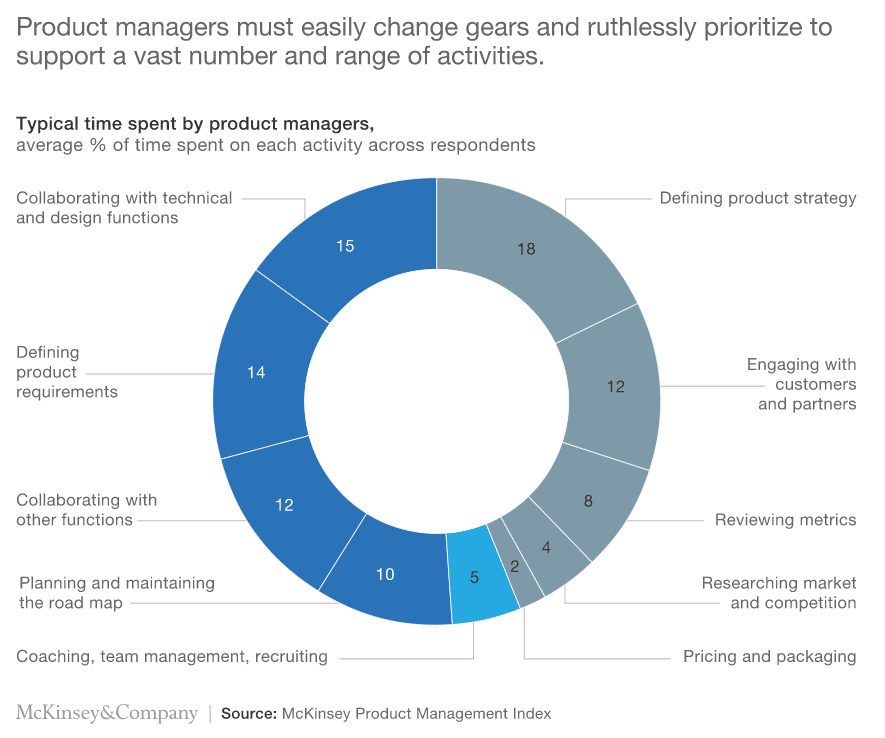
Almost 80% of product managers are involved in design efforts and go-to-market choices, with half of them also making essential pricing decisions, according to a report by McKinsey & Company.
60% of product managers have basic analytics abilities to dive into numbers and draw insights without relying on analysts.
2. How to become a product manager?
There are two ways to become a product manager – follow the conventional way by taking up a product management course or certification and then landing a job.
The other way could be doing courses and building skillsets related to product management by taking up such projects/tasks during work.
Check out our Introduction to Product Management Course from Great Learning Academy which gives you access to 100+ free online courses with certificates to upskill yourself.
3. Is an engineering background necessary to be a product manager?
It is not mandatory to have an engineering degree or background to be a product manager. However, having an engineering background helps you, especially if you are looking for roles in software-related companies.
4. Which industry pays the best salaries for product managers?
Retail, Finance, Manufacturing, E-Commerce, Edu-tech, Travel, Healthcare and Software/IT are a few industries that pay decent salaries for product managers and have many roles related to product management.
5. Which companies generally hire product managers?
Few companies to name are:
- Amazon
- Flipkart
- Mckinsey and Company
- Paytm
- Airbnb
- Microsoft
- Uber
6. How is the future for Product Managers?
The future for Product Managers looks bright, and there has been a lot of career growth opportunities in Product Management over the last 4-5 years. There will be more growth in the upcoming years, considering the rapid technological innovations and advancement.
According to Glassdoor, Product Manager is the 3rd best job in the United States in 2022.
7. Where can I do masters in project management?
You can do the masters or a PG program online as well as offline from any reputed institution/organization.
We recommend you to check out our PG Program in Product Management and Analytics
8. What are some good courses in Product Management?
There are plenty of courses in product management available online. Here are few of the best ones:
- Breaking into Product Management
- Product Management
- Journey of a Pragmatic Product Manager









