Cybersecurity is a vast domain and there are a wide variety of cybersecurity questions that could be asked during an interview. Recruiters mainly focus on the technical aspects and knowledge of tools and techniques to ensure a secure framework. Here are a few commonly requested cybersecurity interview questions that you might face while seeking jobs in the cybersecurity domain.
Cybersecurity Interview Questions for Freshers
1. What is the main objective of Cyber Security?
Cyber Security protects online applications such as computer hardware, software, and data from online threats. Individuals and businesses use the practice to prevent unauthorized access to data centres and other computer programs.
Hence, the main objective of Cyber Security is to provide a secure environment for mobile devices, servers, computers, and data stored on these devices from malicious attackers.
Enroll in Online Post Graduate Programme in Cyber Security, a top-rated Cyber Security course in India that will help you learn important concepts like foundations of information security, cyber-attacks, designing security controls, security operations u0026 incident management with hands-on labs, and capstone projects.
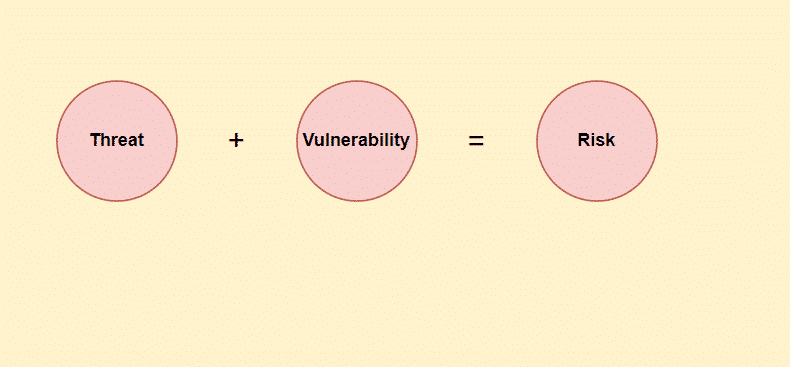
2. Differentiate between threat, vulnerability and risk.
A threat aims to steal or damage an asset. Vulnerability refers to weaknesses in your computer system that might create a pathway for cyber attacks. Risk refers to the damage done to an asset caused by cyber attacks. Risks cannot be removed completely. It can only be reduced.
An essential part of Cybersecurity is managing and mitigating risks. Candidates need to be able to identify risks, assess the impact of those risks, and develop and implement mitigation strategies.
3. What does XSS stand for? How can it be prevented?
XSS stands for cross-site scripting. Cross-site scripting is a cyber-attack where an attacker sends malicious code to a reputable website. It is an attack that can happen only when a website allows a code to attach to its own code. The attacker bundles together two scripts and sends them to the victim. As soon as the script executes, the attacker receives a cookie. With this type of cyber-attack, hackers can collect sensitive data and monitor the activities of the victim.
Ways to prevent cross-site scripting
- Filter input on arrival.
- Encode data on output.
- Use appropriate response headers.
4. What is a Firewall?
A Firewall is a network security device that monitors all incoming and outgoing traffic and permits, blocks, or drops data packets based on a defined set of security rules.
It is also known as a packet filter since it filters the data packets for malicious content.
Popular firewall software is Norton, Netdefender, Glasswire, AVS firewall etc.
Need for Firewall
- Blocks unwanted traffic and malicious software
- Acts as a barrier between computer and outside network
- Secures private information
- Prevents ransomware
- Prevents hacking
5. Define VPN
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. VPN is a secure private network that allows the user to send data in encrypted format from a device to a network over the internet.
6. Who are Black Hat, White Hat and Grey Hat Hackers?
Ethical Hacking is an approach to defending system and network security by exploiting existing vulnerabilities of the same. Ethical hackers strengthen systems and network security by identifying weaknesses and rectifying them with appropriate countermeasures.
The term ‘hacking’ is controversial in nature and is often considered in a negative context. There are different types of hackers that serve different purposes, ranging from malicious to beneficiary. Three different types of hackers are:
- White Hat
- Black Hat
- Grey Hat
White Hat and Grey Hat hackers use their hacking skills for ethical hacking. On the other hand, black hat hackers are involved in illegal hacking and malicious practices. Knowing about different types of hackers will help professionals understand their boundaries as ethical hackers and the legal nuances of being an ethical hacker.
Ethical Hacking Course: Master Hacking Techniques
Enroll in our Ethical Hacking course to learn the latest hacking techniques and cybersecurity skills. Become an expert in ethical hacking today!
7. What are the types of Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity is defined as the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital or virtual attacks.
Types of Cyber Security
- Network Security
- Information Security
- Application Security
- Cloud Security
- Internet of Things Security
- Mobile Security
Network Security
Network security is the process of taking precautionary measures to protect the devices from unauthorized access, modification, or destruction.
Need for Network Security
- The organization’s ability to function without any interference.
- For enabling safe operation in the IT system of any organization.
- To protect the data collected by the organization for their internal use.
Information Security
Information security, also known as infosec is the process of securing data and information secure from any kind of violations in the form of theft, abuse or loss. Information security is based on three main aspects of data security, referred to as the CIA-namely confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Need for Information Security
- To protect the functionality of the organization
- To ensure the safe operation of the application
- To protect the data collected by the organization
Application Security
Application security is the process of increasing the security of web and mobile applications to protect the data from attackers.
Need for Application Security
- To improve the trust among users
- To protect sensitive data
- To maintain the reputation of the brand
- To secure user data from a data breach
Cloud Security
Cloud security is defined as a set of policies and procedures that mainly aims at protecting cloud-based applications and systems.
Need for Cloud Security
- Most companies have decided to migrate their data, applications and other assets to the cloud, now it is very essential to protect this sensitive information that could potentially be exposed.
- Security professionals are more concerned about cloud security in their organization as data leaks can damage customers’ trust.
Internet of Things Security
IoT Security is the process of protecting IoT devices from vulnerabilities.
Need for Internet of Things Security
- IoT devices have to be secure to exchange data. If one device is hacked, the entire network is at risk as all the devices are inter-linked.
Mobile Security
Mobile security is the protection of smartphones, tablets and other various devices from vulnerabilities.
Need for Mobile Security
- To protect private data
- To prevent ourselves from being vulnerable to virus attacks
- To delete sensitive data automatically in case of mobile theft.
- To prevent malvertising
8. What are the benefits of Cyber Security?
Cyber security has excellent benefits. For instance, it saves users from potential cyber-attacks and alerts them of potential dangers. The following is a list of online safety benefits.
- Protects personal and sensitive personal data from organizations and organizations from being stolen.
- The most significant benefit gained from these effective online security measures is the protection of networks in various fake environments that seek to gain unauthorized access to the network.
- The most crucial factor is improving system security in cyberspace.
- Removes the risk of computer hacking, thus reducing the risk of system crashes and crashes.
- It develops complete business security practices using an advanced knowledge framework and facilitates smooth business management activities.
9. What do you mean by a botnet?
A botnet is the short form of a robot network. A botnet is a network of inter-connected devices running on a bot. A bot is a software application program for a particular task. This network is controlled by an attacker.
10. What do you mean by honeypots?
Honeypots are a Cyber Security mechanism that focuses on targeting attackers to study the tricks used by them.
11. Differentiate between Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing.
Vulnerability assessment is the process of identifying security vulnerabilities to understand the weaknesses in a given environment. This is meant for non-critical systems.
Penetration testing is the process of finding vulnerabilities to improve the overall security of the organization. It is also known as pen testing. This process is meant for critical real-time systems. Sensitive data is tested in this process.
12. What do you mean by a Null Session?
A null session occurs when an unauthorized user logs in to a system with no username and password. This usually enables the user to view all the available resources in the network.
13. What are the common types of cyber security attacks?
A cyber-attack is an intentional activity that exploits computers, networks, and enterprises that rely heavily on technology. Cybercriminals use malicious codes to alter the data, logic, or code on the computer.
Top Cyber Security attacks are:
- Phishing Attack
Phishing is the technique to steal a user’s data from the internet or computer-connected device. Login credentials, credit card numbers, and passwords are usually what such hackers obtain from their victims.
- Man in the Middle Attacks
The man-in-the-middle attack is a security breach where cybercriminals place themselves between the communication system of a client and the server. Man-in-the-middle is by far the sneakiest attack by criminals. Vulnerable WiFi connections and communication lines are the easiest means to carry out this security breach.
- SQL Injection Threat
SQL is an acronym for Structured Query Language, and an SQL attack is one of the oldest cybersecurity breaches. In SQL you make queries. Therefore, in the SQL injection threat, the attacker sends a malicious query to the device (a computer, phone, etc.) or a server. The server is then forced to expose sensitive information.
- Distributed Denial of Service
This cyber-attack overwhelms a network, system, or computer with unwanted traffic. The attacker bombards the system or server with high-volume traffic, that its bandwidth and resources cannot handle. Hence, they will not be able to respond to requests. For example, a gardening website that notices a sky-rocketed number of visits of unknown users in a day may be under a DDoS attack.
Distributed Denial of Service attacks does not usually result in identity theft or loss of vital information. However, it will cost a lot of money to get the server running again.
- Drive by Attack
Drive-by attacks are security threats that download unwanted materials from a website. It is also one of the most common ways of spreading malware. All the hacker has to do is to plant code on the page. You have probably seen a few pop-ups that do not relate in any way to what you are searching on the internet. Such pop-ups are drive-by attacks.
- Cross Site Scripting
Cross-site scripting is a cyber-attack where an attacker sends malicious code to a reputable website. It is an attack that can happen only when a website allows a code to attach to its own code. The attacker bundles together two scripts and send to the victim. As soon as the script executes, the attacker receives a cookie. With this type of cyber-attack, hackers can collect sensitive data and monitor the activities of the victim.
- Password Attack
A password attack is an attempt to steal passwords from a user. Since passwords are the most common authentication means, attackers are always on the lookout for ways to use this cyber-attack.
- Ransomware Attack
One cyber threat with scary consequences is the ransomware attack. Moreover, in this type of security breach, the malware prevents users from accessing the data they stored on a server or database. The hacker then sends out a threat demanding a ransom, else they would expose or delete the data.
- Eavesdropping Attack
Other names for eavesdropping attacks are snooping, network security threats, or sniffing. It is very similar to the man-in-the-middle attack, but it does not allow a secure connection between the user and a server. Theft of data and information occurs after you send them out, so they do not get across to the server.
Unsecured and weak network transmissions allow this security breach to thrive. Any device within the network is susceptible to an eavesdropping attack from hackers.
- AI-powered Attack
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been making ground-breaking success in recent years. Almost every gadget has some application of AI in it, which heightens the scare of an AI-powered cyber-attack. Such security threats will have the most devastating effects as autonomous cars, drones, and computer systems can be hacked by artificial intelligence. AI can also shut down power supplies, national security systems, and hospitals.
- Malware
Malware is a common type of cyber threat, defined as malicious software which gets installed into the system when the user clicks on a dangerous link or email.
- Zero-day exploit
A zero-day attack is an attack done by hackers when the network, hardware or software vulnerability is announced publicly. They make use of this time to exploit the vulnerabilities before the solution is implemented.
- Advanced Persistent Threats
An advanced persistent threat occurs when an attacker gains unauthorized access to a system or network and remains undetected for a long duration.
14. What do you mean by brute force in the context of Cyber Security?
A brute force attack is made to damage an organization’s reputation or to steal confidential information.
A brute force attack is a trial and error procedure used by hackers to crack passwords and encryption keys to gain unauthorized access. One of the most significant advantages of brute force attack is that it is easy to implement, and its disadvantage is that it is slow. Brute force attacks can be prevented by increasing the strength of passwords by using multi-factor authentication and limiting failed login attempts.
15. What do you mean by Shoulder Surfing?
Shoulder surfing is a situation where the attacker views the victim’s screen and keypad to obtain confidential information. This attack requires the attacker to be physically next to the victim.
16. Differentiate between hashing and encryption
Hashing is a fast process of mapping arbitrary-sized data into a fixed-size value using hash function.
It is more secure compared to encryption.
Example- MD5, SHA256
Encryption is the process of securing digital data using mathematical techniques with the help of a key used to encrypt and decrypt the data. The encryption key is the heart and soul of the encryption process, a string of characters generated based on various encryption algorithms. Encryption is the process of converting plaintext into Ciphertext. Plain text is data in a readable format, and Ciphertext is data in an unreadable format. Encrypted data is called Ciphertext, whereas unencrypted data is called plain text.
Example- RSA, AES, and Blowfish.
17. What do you mean by two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication is the process of authenticating the user in two steps. It provides additional security for sensitive data. It protects the user against attacks such as phishing, social engineering, and password attack and secures the user’s login.
18. How can you avoid a brute force attack?
Brute force attacks can be avoided by increasing the strength of passwords by using multi-factor authentication and limiting failed login attempts.
19. What do you mean by Man-in-the-Middle Attack?
The man-in-the-middle attack is a security breach where cybercriminals place themselves between the communication system of a client and the server.
Types of Man-in-the-middle attacks
- Session hijacking: In this cyber-attack, the hacker takes control of the session between the network server and the victim. For instance, the hacker can replace the user’s connection, or even create a fake server and trick the victim into connecting to it.
- IP spoofing: This security breach provides access to the hacker by tricking the user into communicating with a known entity. For instance, a packet of internet addresses, including that of a trusted site like google, can be sent to the victim.
- Replay: In this Man-in-the-middle threat, the hacker saves old messages and then uses it later to impersonate the user. For example, if a hacker gets hold of your Instagram page, he or she can use it to impersonate you.
20. Differentiate between Information protection and information assurance.
Information protection focuses on information security whereas information assurance focuses on the quality, reliability, and accuracy of information.
Cybersecurity Interview Questions for Experienced
21. Differentiate between VPN and VLAN
VPN stands for virtual private network and VLAN stands for virtual local area networks. VPN focuses on providing a secure private network to employees whereas VLAN focuses on grouping geographically separated devices together to improve the communication between devices. It also focuses on providing a simple network that facilitates the network administrators to modify the network.
22. What do you mean by perimeter-based and data-based protection?
Perimeter-based protections refer to setting up security around a perimeter to secure systems from unauthorized users. Data-based protection refers to securing confidential data from unauthorized users.
23. Which is more reliable: SSL or HTTPS?
SSL stands for secure sockets layer and HTTPS stands for hypertext transfer protocol secure. HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP. SSL is a part of the HTTPS protocol. Both are encryption protocols but they have different approaches.
HTTPS protocol is a combination of HTTP and SSL protocols that encrypts data. SSL encryption online communication. SSL is more secure and reliable when compared to HTTPS. SSL works on top of HTTP in terms of providing security.
24. What do you mean by a DDoS attack? How can you prevent it?
DDoS attack overwhelms a network, system, or computer with unwanted traffic. The attacker bombards the system or server with high-volume traffic, that its bandwidth and resources cannot handle. Hence, they will not be able to respond to requests. Distributed Denial of Service attacks does not usually result in identity theft or loss of vital information. However, it will cost a lot of money to get the server running again.
Ways to prevent DDoS attacks
- Create a good DDoS response plan
- Have a good knowledge of the network traffic
- Ensure to make the network resilient
- Good cyber hygiene should be maintained
- Understand the consequences of an attack
25. Differentiate between IDS and IPS in the context of Cyber Security.
IDS stands for intrusion detection system and IPS stands for intrusion prevention system. IDS is a system that monitors network traffic and reports issues if any suspicious activity is detected. IPS is a network security tool that monitors network traffic and prevents malicious content from reaching the target.
The major difference between IDS and IPS is that IDS is a monitoring system and IPS is the control system. IDS doesn’t prevent the data packets but IPS prevents the data packets from reaching the target if any malicious content is found.
26. What do you mean by Network Sniffing?
Network sniffing is the process of monitoring network traffic. A network sniffer is a tool used to monitor the data flowing over the network.
27. Differentiate between Black Box Testing and White Box Testing.
Black box testing is a software testing process in which the implementation of the item being tested is not known to the tester. White box testing is a software testing process in which the implementation of the item being tested is known to the tester.
28. What do you mean by System Hardening?
System Hardening is the process of securing computer systems from cyber attacks.
29. Differentiate between HIDS and NIDS.
HIDS stands for host intrusion detection system and NIDS stands for network intrusion detection system.
HIDS focuses on host based behaviours such as what files are accessed and which apps are utilized whereas NIDS focuses on network traffic to monitor suspicious activity.
30. What do you mean by Domain Name System (DNS) Attack?
In a DNS attack, the attacker tries to compromise a network’s DNS and takes advantage of the vulnerabilities in DNS.
Role of DNS: Every website is connected with an IP address, a 16-digit number, and it is difficult to remember the IP address for each website. So there is a mapping between IP address and Domain names for each website. Every domain name in the DNS will nominate a set of name servers to be authoritative for its DNS records. For example, when a Web address or URL is typed into a browser, a DNS query learns an IP address of a Web server associated with that Domain name.
31. Differentiate between Stream Cipher and Block Cipher.
In-Stream cypher, one byte of data is converted at a time from plain text to Ciphertext.
It processes 8 bits of data at a time.
In Block cipher, blocks of plain text are converted into blocks of Ciphertext.
The block size depends on the algorithm, but it shouldn’t be too large or small. It should be multiples of eight, and it usually processes 64 bits or more.
Block cipher is simple but slower when compared to a stream cipher.
32. Differentiate between spear phishing and phishing?
This is one of the important cybersecurity interview questions asked in the interview
Spear phishing: Spear phishing is the more targeted version of phishing as it is much harder to detect and has a high success rate. This requires much effort by the attacker to make it look less conspicuous.
Phishing : The phishing attack is a very common one and is executed via phone or email. This creates a sense of urgency like your password has expired and you need a quick fix, or your bank details are not correct, and you need to update urgently as it will result in blocking your card. Such an email would be identical. They will ask for urgent action, which usually leads to victim panic. In such a situation, the victim usually makes a mistake by clicking on the link provided in the email or text message. Such websites are replicas of new ones, and they are created to target specific victims who will end up entering their correct information.
33. What do you mean by ARP poisoning?
The acronym ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) which is a communication protocol used to find the MAC (Media Access Control) address of a host from its IP address. It is an important protocol in networking used to convert a 32-bit Internet Protocol (IP) address, typically for IPv4, to a 48-bit MAC address in a LAN.
ARP poisoning is also known as ARP spoofing.
ARP poisoning is a type of man-in-the-middle attack that focuses on blocking the communication between network devices.
34. What do you mean by SQL Injection? How do you prevent it?
This is one of the important cybersecurity interview questions asked in the interview
SQL is an acronym for Structured Query Language, and an SQL attack is one of the oldest cyber security breaches. In SQL you make queries. Therefore, in the SQL injection attack, the attacker sends a malicious query to the device or a server. The server is then forced to expose sensitive information.
For instance, a cybercriminal can create a query that disrupts and gets into the database of your webpage through SQL injection. All the data, like your customers’ details, amount paid, and other confidential information, can then be released by the query. The daunting part of this cyber-attack is that the attacker can not only get hold of sensitive information but also alter or wipe them completely.
Ways to prevent SQL Injection attack
- Validate User Inputs
- Sanitize Data By Limiting Special Characters
- Enforce Prepared Statements And Parameterization
- Use Stored Procedures In The Database
- Actively Manage Patches And Updates
- Raise Virtual Or Physical Firewalls
- Harden Your OS And Applications
- Reduce Your Attack Surface
- Establish Appropriate Privileges And Strict Access
- Limit Read-Access
35. What is the difference between a virus and a worm?
A virus is a malicious program that infects an application in the system by replicating itself.
A computer worm is a malicious program that replicates itself to eat up system resources.
36. What form of cookie might be used in a spyware attack?
Third party cookies are used in spyware attacks. They usually come from a different website that the user isn’t currently using. Advertisers monitor the online activities of users and utilize them to make money it by selling them.
37. What is CTI?
This is one of the important cybersecurity interview questions asked in the interview
CTI stands for Cyber Threat Intelligence. Cyber threat intelligence is the amount of data that becomes cyber threat information that is collected, evaluated in the context of its source, and analyzed through rigorous and firm tradecraft techniques by industry experts.
The information refers to the data that organizations collect and use to better understand past, present, and future threats of the market and the customer’s information. The information that the organizations possess has the context to the operations of an organization’s business network and helps identify potential cyber-attacks and prevents future threats.
To understand better, take Cyber Threat Intelligence Quiz.
38. What are Polymorphic viruses?
Polymorphic viruses are computer viruses that affect data types and functions. It is designed to avoid being detected by scanner.
39. What do you mean by Active reconnaissance?
Active reconnaissance is a process where hackers attack a computer system by targeting vulnerabilities to gain sensitive information.
40. What are the impacts of Cyber attacks?
A lack of focus on cybersecurity can most often cause serious damage in various ways including:
- Economic costs: This involves the theft of intellectual property, corporate information, disruption in trading and the cost of repairing damaged systems.
- Reputational costs: This includes loss of consumer trust and loss of future customers to competitors due to poor media coverage.
- Regulatory costs: GDPR and other data breach laws can impact an organization to suffer from regulatory fines or sanctions due to these cybercrimes.
Given the nature of these cyber-attacks, it is vital for all businesses, regardless of the size, to understand cybersecurity threats and methods to mitigate them. This includes regular training on the subject, and a framework to work with – that aims to reduce the risks of data leaks and breaches.
41. What is Data Leakage?
This is one of the important cybersecurity interview questions asked in the interview
The unauthorized transmission of data from within an organization to an external entity or destination is known as data leakage.
The many factors that contribute to data leakage are:
- Weak passwords
- Theft of company assets
- The exploitation of vulnerabilities by Hackers
- Accidental e-mails
- Malicious attacks
- Loss of paperwork
- Phishing
- System errors or misconfiguration
- Inadequate security features for shared drives and documents
- Unsecured back-up
Cybersecurity Interview Questions
The most common data loss prevention techniques are:
- Encryption
- Cryptographic hashing
- Encoding
- Data fingerprinting (read, hash and store)
Vulnerability is the gap or weakness in a security program that could be exploited to acquire unauthorized access to a company’s assets.
A threat is anything that can intentionally or accidentally exploit a vulnerability to damage or destroy an asset.
Risk is the potential of a threat to exploit a vulnerability and destroy or damage an asset. If a system is not secure enough and has the chance of data loss or damage, it’s at high risk.
42. What are the different types of web server vulnerabilities?
This is one of the important cybersecurity interview questions asked in the interview
Some of the web server vulnerabilities are:
- Misconfiguration
- Default Settings
- Bugs in Operating System or web server
43. What is SSL? Is it enough when it comes to encryption?
SSL is not hard data encryption. It is an identity verification technique to understand that the person one is conversing with is in fact who they say they are. SSL and TLS are used almost everywhere and by everyone, and because of this popularity, it faces the risk of being attacked via its implementation and its very known methodology (eg.: The Heartbleed bug). Additional security is required for data-in-transit and data-at-rest, as SSL can be easily stripped in certain circumstances.
44. Describe the 3 major first steps for securing your Linux server.
The three broad steps to secure a Linux Server are:
Auditing - A server audit is performed to find obscure issues that can challenge the server's security or stability. The system is scanned or audited for security issues using a tool called Lynis. Each category is separately scanned and a hardening index is subsequently provided to the auditor to take further actions.
Hardening: Once the audit is complete, the system needs to be hardened based on the security level it requires. This process mainly involves taking the right steps against the security issues identified while auditing.
Compliance: Sticking to the policy outline and the technical baseline is an important aspect of security to maintain a common standard for the same.
45. What are the techniques used in preventing a brute force login attack?
This is one of the important cybersecurity interview questions asked in the interview
There are three techniques to prevent a Brute force login attack:
Account Lockout Policy: After a set number of failed attempts the account is locked out until the administrator unlocks it.
Progressive Delays: After three failed login attempts, the account will be locked for a certain time period. With each failed login attempt after this, the lock-out period will keep increasing, hence making it impractical for the automated tools to attempt forced login.
Challenge-response test: This is primarily to prevent automatic submissions on the login page. Tools like free reCaptcha can be used to ask the user to manually input some text or solve a simple problem to ensure that a user is an actual person.
46. What is Phishing and how can it be prevented?
Phishing is a social engineering attack intended to steal data from users. The data attacked is usually the login credentials, credit card numbers, and bank account details with an intention to deceit or scam users. The social engineer impersonates genuine web pages and asks for login and other details.
Some of the ways to prevent phishing are:
- Two-factor Authentication involving two identity confirmation methods
- Filters to flag high-risk e-mails
- Augmented password logins using identity cues
- Train your employees to beware of certain tell-tail e-mails, and on information sharing tactics
- Have a guard against Spam
47. What is a CIA triad?
This is one of the important cybersecurity interview questions asked in the interview
It is a standard for implementing Information Security and is common across various types of systems and/or across organizations.
Confidentiality: Only the concerned audience can access the data.
Integrity: Ensures that data is kept intact without any foul play in the middle
Availability: Of data and computers to authorized parties, as needed
48. Explain SSL encryption
Secured Sockets Layer is the standard to establish an encrypted link between a browser and a web server. It secures the data exchanged between the web server and the browser, and keeps it private and integral. SSL is the industry standard to protect online transactions between businesses and their respective customers and is used by millions of websites.
49. What are salted hashes?
A password is protected in a system by creating a hash value of that password. A ‘salt’ is a random number which is added to this hash value and stored in the system. This helps against the dictionary attacks.
50. What are some common cyber-attacks?
Some of the most common cyber-attacks are:
- Phishing
- Malware
- Password Attacks
- DDoS
- Man in the Middle
- Drive-By Downloads
- Malvertising
- Rogue Software
51. How does tracert or tracerout work?
These are used to determine the route from the host computer to a remote machine. They also identify how packets are redirected, if they take too long to traverse, and the number of hops used to send traffic to a host.
52. What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
In symmetric encryption, a single key is used for both encryption and decryption. While asymmetric encryption uses different keys. Also, symmetric is much faster but is more difficult to implement as compared to asymmetric.
53. Is it possible to log in to Active Directory from Linux or Mac box?
Yes, it is possible to access the active directory from a Linux or a Mac box system by using the Samba program for implementing the SMB protocol. Depending on the version, this allows for share access, printing, or even Active Directory membership.
To conclude
Stay tuned to this page for more information on cybersecurity interview questions and career assistance. If you are not confident enough yet and want to prepare more to grab your dream job in the field of Advanced Computer Security, upskill with a Cybersecurity Course.