Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming how we live, work, and connect with each other. From self-driving cars on the highway to medical tools that detect diseases early, AI is everywhere.
In this article, we’ll explore what AI actually is, the main types of AI, a quick history of how we got here, and practical examples showing how AI powers everyday life.
We’ll also discuss the ethical questions that come with such a fast-growing field and look at what the future might hold.
Definition of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence or AI refers to machines that mimic human intelligence – things like problem-solving, pattern recognition, language understanding, learning from experience, and decision-making.
In other words, AI systems are built to do tasks that require human smarts, like analyzing images, translating languages, or making recommendations.
Over the years, AI has branched out into specialisms like:
- Machine Learning (ML): Where systems learn from data and get better over time.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Technology that helps machines understand and respond to human language.
- Deep Learning: A more advanced subset of ML that uses layers of artificial neural networks to process massive amounts of data and make increasingly accurate predictions.
How Does AI Work?
AI works by copying human intelligence using computer code. It relies on three main processes:
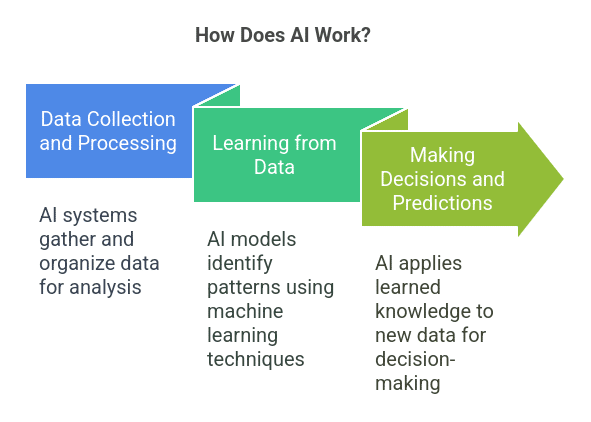
1. Data Collection and Processing
AI systems gather large amounts of data. This can be text, images, audio, or numbers, and then clean and organize it for analysis.
2. Learning from Data
Using machine learning, the AI models look at the data and find patterns and relationships. Techniques like neural networks, deep learning and reinforcement learning allow the systems to get better over time. Essentially, the algorithms learn from experience just like we do from practice.
3. Making Decisions and Predictions
Once trained the AI can apply what it has learned to new data. This allows it to do things like recognize images, understand natural language, or make predictions. The system adjusts its output based on feedback and refines its performance and accuracy.
In short, AI combines data, algorithms, and iterative feedback to do complex tasks, often in the same way we do.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
AI can be categorized by its capabilities and by how it functions.
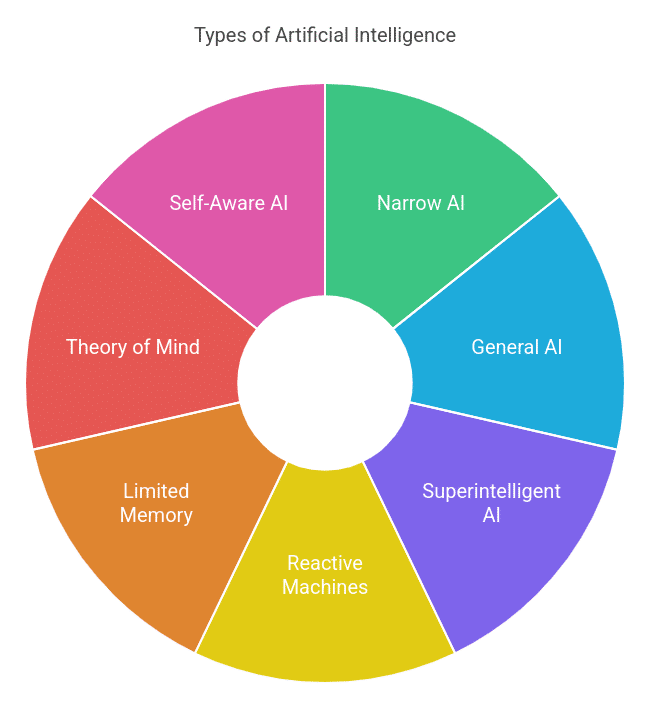
1. Based on Capabilities
- Narrow AI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence – ANI): This is the most common type of AI today, designed for one specific job. Examples include facial recognition systems, internet search algorithms, or self-driving car software. They’re great at their assigned tasks but can’t handle anything outside of their specialty.
- General AI (Artificial General Intelligence – AGI): This is the theoretical “holy grail” of AI: a system that can perform any intellectual task a human can. AGI would learn, reason, and solve problems across multiple areas—just like a person. Right now, it’s still a concept rather than a reality.
- Superintelligent AI (Artificial Superintelligence – ASI): This level of AI, if achieved, would surpass human intelligence in virtually every aspect—like science, art, and creativity. ASI is speculative and mostly discussed in academic and futurist circles.
2. Based on Functionality
- Reactive Machines: The simplest kind of AI, which responds to immediate inputs without using past experience. IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess computer that beat a grandmaster, fits this category because it made decisions strictly based on its current board position—no long-term memory involved.
- Limited Memory: These AI systems look at historical data to help make decisions in the present. Self-driving cars use Limited Memory AI to learn from past driving experiences so they can navigate roads and traffic more effectively in real-time.
- Theory of Mind: A concept still under development, Theory of Mind AI aims to understand and respond to human emotions, intentions, and interactions. Think of it as AI that’s not just “smart” but also “socially aware” of the people around it.
- Self-Aware AI: This is another hypothetical concept where an AI system would be self-aware and know it exists. It’s a topic of much debate for both the technical and ethical implications.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is AI that creates new content – text, images, music or even video – that looks like the data it was trained on.
Unlike traditional AI that might analyze or classify existing data, generative AI uses techniques like GANs or transformer models (e.g. GPT series) to produce original content.
History of Artificial Intelligence
AI has been around since the mid-20th century with major milestones that got us here:
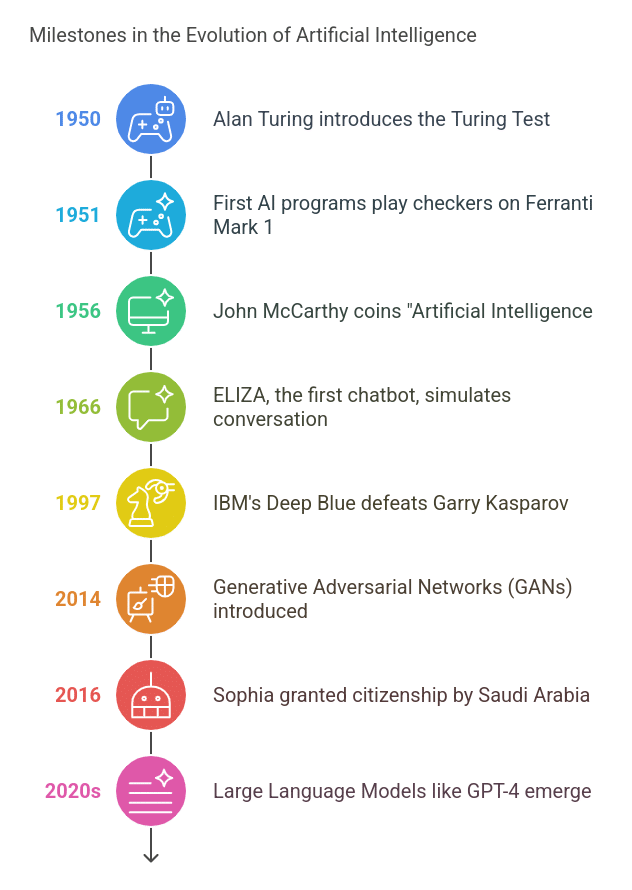
➡️ 1950: Alan Turing published “Computer Machinery and Intelligence,” introducing the Turing Test to see if a machine’s behavior could be indistinguishable from a human’s.
➡️ 1951: The first AI-like programs were built to play checkers on the Ferranti Mark 1, showing computers could handle tasks once thought too difficult for machines.
➡️ 1956: John McCarthy coined the term “Artificial Intelligence” during the Dartmouth Conference, officially launching AI as a field of study.
➡️ 1966: ELIZA, the first chatbot, revolutionized human-computer interaction by showing machines could simulate human conversation in a basic form.
➡️ 1970s–1980s: Expert systems emerged, using rule-based reasoning to solve problems in specialized domains. XCON was an early commercial success, deployed in the 1980s.
➡️ 1997: IBM’s Deep Blue famously beat world chess champion Garry Kasparov, a defining moment for AI’s potential in strategic decision-making.
➡️ 2014: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) arrived, opening the door to creating synthetic data—everything from realistic images to deepfake videos.
➡️ 2016: Sophia, a humanoid robot by Hanson Robotics, became the first robot to be granted citizenship by Saudi Arabia and raised questions about AI’s social and ethical impact.
➡️ 2020s: Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Google’s Gemini made language processing more natural and enabled AI to interact with humans for tasks like customer service, content creation and more.
Examples and Applications of AI
AI is already in our daily lives, changing everything from healthcare to logistics. Here are some examples and uses:
Healthcare
- Predictive Models: Scanning for early signs of illnesses like cancer, AI algorithms can alert doctors sooner and better patient outcomes.
- Medical Imaging: AI tools can interpret X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with incredible accuracy, catching what the human eye might miss.
- Surgical Assistance: Robotics guided by AI help surgeons during operations with better accuracy and fewer complications.
- Personalized Medicine: By analyzing genetic profiles and patient records, AI tailors treatment plans for better effectiveness.
Finance
- Fraud Detection: Real time AI analysis of transaction patterns flags suspicious activity before it gets out of hand.
- Robo-Advisors: Automated investment platforms help people manage their portfolios by giving them personalized financial advice.
- Risk Management: AI models assess credit risk and optimize portfolios so investments are stable and profitable.
Retail
- Personalized Recommendations: AI sifts through shopping data to suggest products that match individual tastes, sales, and customer loyalty.
- Inventory Management: By analyzing sales trends, AI helps retailers keep the right amount of stock, costs, and waste.
- Customer Support: AI chatbots handle questions and provide 24/7 support, with faster response times and better satisfaction.
Transportation
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use AI to make decisions in real-time, from speed to obstacle detection.
- Traffic Management: AI optimizes traffic lights and public transport schedules, less congestion and travel time.
- Predictive Maintenance: Intelligent systems can predict mechanical issues, and fleet owners can fix problems before they become critical.
Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can pinpoint when machines will break down, and maintenance teams can fix issues before they stop production.
- Quality Control: Computer vision can spot defects on the production line, and fewer faulty products reach the customer.
- Supply Chain Optimization: By streamlining logistics and inventory, AI can deliver products faster and cheaper.
Energy
- Smart Grids: AI balances electricity supply and demand, less waste, and no power outages.
- Renewable Energy: By analyzing weather data, AI can make wind turbines and solar panels more efficient and clean energy.
Human Resources
- Recruitment: AI filters resumes and matches candidates to the right roles, fast-tracking the hiring process.
- Employee Engagement: By looking at workforce data AI can predict job satisfaction and retention, so companies can keep morale high.
Ethical Considerations in AI
As AI moves forward, it raises big questions:
- Bias and Fairness: AI can inherit the biases in its training data. This can lead to unfair decisions in hiring, lending or law enforcement. Making sure AI is bias-free is a top priority.
- Privacy and Data Security: Because AI relies on massive datasets—often containing personal info—user privacy is key.
- Accountability: The more AI decides on its own the harder it is to assign blame. Transparent and accountable design is essential.
- Job Displacement: As automation grows workers in roles like manufacturing or customer service may lose their jobs. Society needs to plan for these changes and support the affected workers.
Also Read: Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Conclusion
From the early days of simple reactive machines to the dream of super-intelligent AI, AI has been advancing and hitting major milestones along the way. Right now, AI is in industries like healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and more—cutting costs, streamlining operations, and improving our daily lives.
However, as AI gets more powerful, setting up ethical guidelines and ensuring responsible development is critical. We need to ask questions about bias, privacy, and accountability. Ultimately, AI’s potential is limitless, and by guiding its progress, we can have safer roads, better healthcare, smarter tools, and a brighter future.
Are you looking to enhance your career in AI?
Check out our PG Course in Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning, crafted to provide you with the job-ready skills in Generative AI, Agentic AI, and more.
To understand basic AI concepts, consider taking free AI courses.