Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the way we live and work, becoming an integral part of our everyday lives. From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to powerful tools that predict trends and solve complex problems, AI is remarkably reshaping industries and society.
But with great power comes great responsibility—and debate. While many see AI as a force for innovation and progress, others worry about its impact on jobs, privacy, and ethics.
In this article, we’ll dive into AI’s pros and cons, exploring its potential to drive positive change while considering the challenges it brings.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
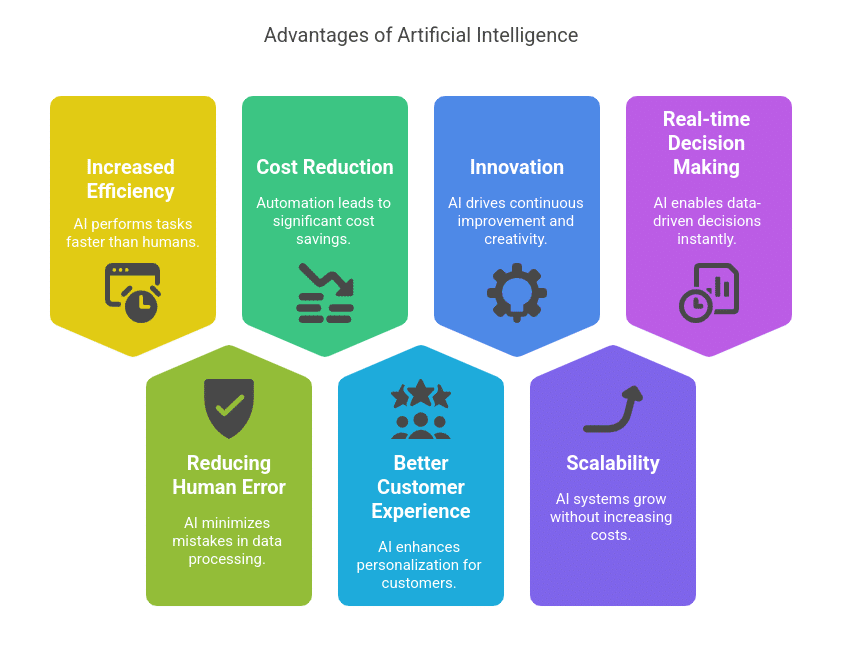
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
AI can do tasks way faster than humans do. For example, in healthcare AI systems can analyze medical images and detect abnormalities in seconds, where it would take human radiologists longer.
AI can also automate repetitive and mundane tasks faster and more accurately, freeing human resources for more complex and creative endeavors. For example, AI-driven robots in manufacturing facilities can perform assembly line tasks with remarkable precision and efficiency.
2. Reducing Human Error
By processing data and making decisions, AI minimizes human mistakes. In finance, AI algorithms can process millions of transactions with a much lower error rate than manual processing. For example, AI-driven coding systems in healthcare have reduced coding errors by up to 35%, with big potential to improve billing accuracy and operational efficiency.
3. Cost Reduction
The automation of AI can save you operational costs, so you can optimize your budget. For example, chatbots in customer service can handle a lot of inquiries at once, so you don’t need to have a massive human staff, and you’ll see cost savings in labor and operational expenses.
4. Better Customer Experience
AI delivers better customer service through personalization, so you get higher satisfaction rates and engagement. Companies like Netflix and Amazon use AI to provide personalized recommendations based on user behavior. This hyper-personalization keeps viewers on Netflix for longer and increases customer satisfaction and retention on Amazon.
5. Innovation
Adopting AI drives innovation across many tech fields and creates an environment of continuous improvement and creativity. In the automotive industry, AI is key to the development of self-driving cars.
Recent advancements include the integration of AI and machine learning for real-time decision-making in complex urban environments and end-to-end models for fully autonomous vehicles. (source)
6. Scalability
AI systems are highly scalable, and businesses can grow without a proportional increase in cost or resources. For example, cloud-based AI platforms can scale to process vast amounts of data in real-time for global e-commerce operations and still perform consistently even during peak shopping events.
7. Real-time Decision Making
AI helps organizations make data-driven decisions in real-time by processing and analyzing data. In logistics, AI algorithms can optimize route planning and delivery schedules in real-time.
For example, an AI system used by a global shipping company adjusts delivery routes in real-time based on live traffic updates and weather conditions and has resulted to 20% improvement in delivery efficiency.
Also Read: Top Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Summary Table of Advantages
| Advantage | Description | Example |
| Efficiency | Performs tasks faster than humans, significantly reducing work time. | AI-powered medical image analysis |
| Reducing Human Error | Minimizes mistakes in data processing. | AI-driven financial transaction processing |
| Cost Reduction | Lowers operational costs through automation | AI chatbots in customer service |
| Enhanced Customer Experience | Improves service delivery via personalization | AI-powered recommendation systems |
| Innovation | Fuels technological advancements, leading to significant improvements in self-driving car algorithms and sensor technologies | AI in self-driving car development |
| Scalability | Facilitates business growth without significant cost increases by leveraging cloud-based AI solutions | Global e-commerce platforms managing surge in demand during peak seasons |
| Real-time Decision Making | Enables rapid, data-driven responses to dynamic market conditions, optimizing operational processes instantly | AI systems in logistics adjusting routes based on live data |
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
1. Biases
AI can perpetuate and even worsen existing biases in the data. For example, facial recognition systems have higher error rates for certain ethnic groups due to biased data. Studies have shown significant disparities in error rates, with error rates for dark-skinned women reaching 34.7% compared to 0.8% for light-skinned men.
2. Unemployment
AI-driven automation may displace jobs, although new roles are emerging in technology-based fields.
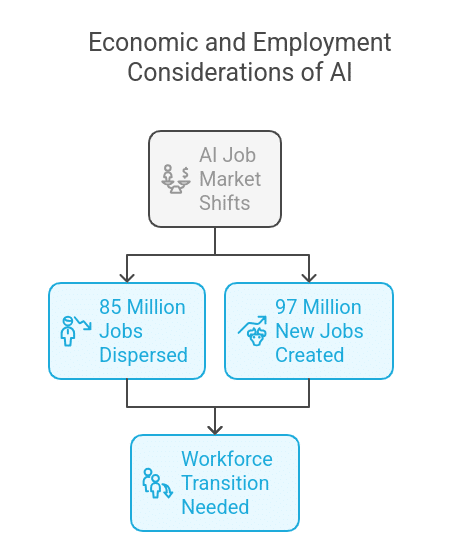
The World Economic Forum says by 2025, AI will displace 85 million jobs, while 97 million new roles will emerge. Specific sectors like manufacturing will be more vulnerable to job losses, while industries like tech and health will see job creation due to AI-driven innovation.
Also Read: How to Start a Career in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
3. Ethical Dilemmas
AI introduces complex ethical problems, especially regarding accountability and transparency. For example, using AI in criminal justice systems to predict recidivism rates raises questions about fairness and accountability. Ethical issues vary by country, but bias, lack of transparency, and discrimination are common across most legal systems.
4. Cost
While AI will reduce operational costs in the long run, the initial implementation can be expensive due to technology and talent investments. Small to medium businesses struggle with the high upfront cost of AI implementation which can range from $5,000 to $200,000 or more depending on the complexity and scope of the project. Ongoing maintenance and upgrades add to the cost.
5. Privacy
The amount of data AI requires raises significant privacy issues that must be addressed through proper safeguards and compliance frameworks. Effective privacy methods include anonymization, pseudonymization, encryption, and differential privacy. Organizations must also comply with regulatory requirements and get user consent to mitigate the privacy risks of AI systems.
6. Security Risks
As AI systems become part of critical infrastructures, they also introduce new security challenges. For example, autonomous AI systems managing power grids or financial transactions can be targeted by sophisticated attacks, which can lead to systemic failures. One example is a simulated attack on an AI-managed industrial system in which attackers exploited vulnerabilities.
7. Over-reliance on Automation
Overreliance on AI may erase human skills and critical thinking. In the aviation and health sectors, excessive AI automation has raised concerns about human oversight, which is critical in emergencies where human judgment is needed. For example, overreliance on automated decision-support systems has delayed human intervention in unexpected events in air traffic control situations.
Summary Table of Disadvantages
| Disadvantage | Description | Example |
| Bias | Perpetuates existing biases in data; leads to unfair outcomes | Gender Shades study found higher error rates for darker-skinned women in facial recognition systems |
| Unemployment | Can lead to job losses, despite the creation of new tech-centric roles | Projected job displacement of 85 million jobs by 2025, with 97 million new roles created |
| Ethical Concerns | Raises issues regarding accountability, transparency, and decision-making | Ethical debates over AI in criminal justice prediction systems and their implications for fairness |
| Cost | High initial implementation costs | AI projects for small businesses can range from $10,000 to over $200,000; large enterprises may spend millions |
| Privacy | May infringe on personal data protection and privacy rights | Apple’s $95 million settlement over Siri privacy infringement; GDPR compliance issues for voice assistants |
| Security Risks | Exposes systems to cyber threats as AI becomes embedded in critical infrastructure | Simulated attacks on AI-managed industrial systems highlighting potential vulnerabilities |
| Over-reliance on Automation | Excessive dependence on AI may diminish human oversight and critical thinking in emergencies. | Instances in aviation and healthcare where automated systems delayed human intervention during critical events |
Strategies and Considerations
AI Bias Mitigation
To reduce bias:
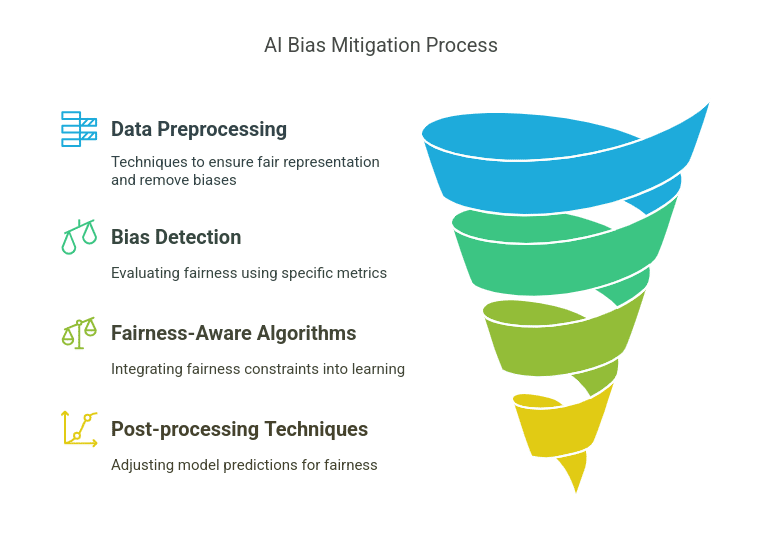
- Data Preprocessing: Use techniques like Preferential Sampling and Massaging to rebalance and augment datasets to ensure fair representation and anonymization to remove sensitive attributes.
For example, researchers at MIT have developed ways to remove gender bias from word embeddings used in NLP. Synthetic data augmentation is also promising in reducing biases.
- Bias Detection Metrics: To evaluate fairness, use metrics like disparate impact, equal opportunity difference, and demographic parity. These metrics have varying reliability and accuracy, and some are more suitable for specific contexts. Google’s What-If Tool helps developers test for bias in machine learning models.
- Fairness-Aware Algorithms: Techniques like adversarial debiasing and fairness-aware regularization are being implemented. Recent work in this area focuses on integrating fairness constraints into the learning process to ensure fair outcomes.
IBM’s AI Fairness 360 toolkit has a set of metrics for datasets and models to check for unwanted bias.
- Post-processing Techniques and Auditing: Implement equalized odds post-processing, which adjusts model predictions to align the rates of true and false positives across demographic groups.
Regular auditing of model outputs is important, and the best practice is to audit frequently with independent third-party auditors to ensure objectivity. Third-party auditors face challenges like transparency, data privacy, and the need for robust frameworks.
These, when done right, can significantly reduce bias in AI systems and ensure fairness across demographic groups.
Privacy by Design
Privacy in AI development means:
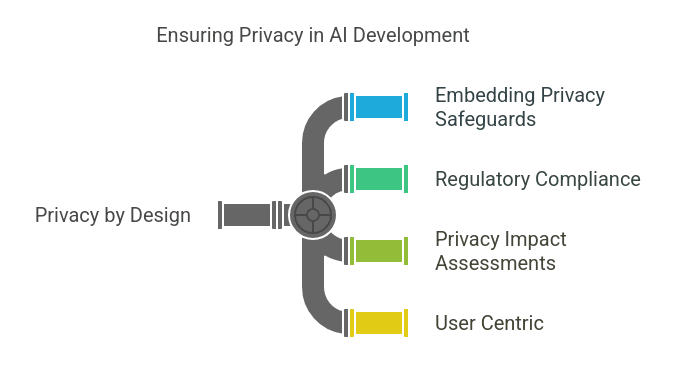
- Embedding Privacy Safeguards: Privacy protocols must be embedded at the very start of AI design. Differential privacy is an example. Apple has it in its iOS. It means data is collected in a way that individual user data is anonymous, balancing data utility with user privacy.
- Regulatory Compliance: Complying with frameworks like GDPR is key to protecting individual privacy rights. Companies like Microsoft have tools to help you assess your AI systems for GDPR compliance. These tools track data processing, manage consents and data minimisation.
- Privacy Impact Assessments: Regular assessments are critical to identify and mitigate privacy risks. The UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office has great guidance on how to do this. These assessments help you evaluate your data protection strategy and implement the necessary safeguards.
- User Centric: Design systems that put user privacy first. Signal’s end to end encryption for messaging is an example of this. Only the intended recipient can see the communication, so user privacy and security is maintained.
Economic and Employment Considerations
- Job Market Shifts: The World Economic Forum says AI will dispense 85 million jobs by 2025 and create 97 million new ones. We need to transition our workforce accordingly. This is happening in sectors like manufacturing, where robotic process automation is creating new roles for robot programmers and maintenance technicians.
- Cost Savings vs. Investment: Organizations receive different amounts of cost savings from AI. Some receive a lot, and some receive little. The initial investment can be large. Managing these costs includes tracking return on investment (ROI) and optimizing costs through smart deployment.
For example, Bank of America reported $2 billion in annual savings from its AI and cloud automation initiatives.
Conclusion
AI has both huge benefits and big challenges. On the plus side, it is efficient, reduces human error, saves costs, improves customer experiences, and drives innovation. On the minus side, it raises issues of bias, job displacement, ethics, high initial cost, and privacy risks.
Advancements in explainable AI will shape the future of AI, aiming to make AI decision-making more transparent and understandable. Robust regulatory frameworks and international cooperation will be key to addressing AI’s global impact.
Want to build a career in AI and Machine Learning?
Advance yourself with the UT Austin’s AIML Course. Gain in-depth knowledge of AI, Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning while earning dual certificates from world-class faculty and industry experts.