There is one thing that you will agree with me—that the fourth industrial revolution is here, thanks to AI and Big Data. In fact, according to a report done by CNN there is no accurate figure on the amount of data in Big Data. It is estimated that more than 90% of all data existing right now was created last year – and it keeps increasing.
Even though this is a lot of data, it is useless in its raw form. This is where AI comes in to make sense of the data. As a result, more companies are now embracing AI. According to a survey done by New Vantage Partner more than 95% of Fortune 1000 executives in sixty companies were investing in AI and Big Data. Artificial intelligence and Big Data have revolutionized every industry and companies are continually seeking out ways to make AI and Big Data work for them.
AI, Big Data and soft drinks
Everyday people consume 1.9 billion servings of Coca Cola drinks. Due to this huge market share in the beverage space, Coca Cola generates a lot of data that it uses to make strategic decisions. Coca Cola was the earliest non-IT company to adopt AI and Big Data.
Coca Cola is known for investing heavily in research and development. After having a successful launch of self-service soft drinks and fountains, Coca Cola gathered all this data. It then combined it with AI and using the insights acquired it launched a new beverage brand—Cherry Sprite. Cherry Sprite was based on the data collected by clients mixing their drinks to create the perfect cocktail beverage.
AI, Big Data and Education
Elsevier is one of the global leaders in the publishing of medical and scientific information. Over the years Elsevier has leveraged AI and Big Data to improve its operations. Due to the massive amount of data that the company has collected in its 140-year existence it has built advanced analytics systems using AI and Big Data.
Traditionally, getting information from any of their publications meant that you had to get a paper-based publication or book. However, as Internet usage spread, Elsevier decided to leverage this and digitize its literature. After digitizing the company saw another challenge – information overload. It is estimated that data in the world doubles every two years.
Not all this data is useful, and Elsevier realized that they needed to find a way to cut through the noise and give their readers valuable and actionable data. This is where AI and Big Data came in. AI and Big data were used to study the reading habits of their clients and analyze which kind of data was being consumed a lot. Using these insights they then deployed machine learning to present relevant information to their readers.
The case for AI, Big Data and Fake News
You have probably heard of fake news where people post false information about others on the Internet. The news could be something as trivial as rumours about one’s dating life to graver news like the death of the same person. Due to the many media outlets like social media, blogs and even traditional media fake news can spread like a wild bush fire, and the truth only comes out later on after the damage has been done.
Fake news is a significant issue, and one Google-funded company is leveraging AI and Big Data to combat fake news. Veri-Flix, a Belgium company, is leveraging AI—with a focus on machine learning to fight fake news. These days citizen-journalism has become a force that even mainstream media institutions cannot ignore. Anyone can upload a video and make fake news about it. By employing machine learning they can scan user-uploaded videos and determining their credibility. This is done by collecting data like video content, time-stamps, and geolocation. Using this data they tag several videos and compare them against each other. After garnering an award and funding from Google the company’s technology is being put to the test at the country’s largest media station.
AI, Big Data and food
McDonald’s, one of the biggest fast-food chains on the planet, is one company that needs no introduction. For a long time, the fast-food chain did not see the need to implement AI and Big Data but upon seeing the success that their competitors were having, they revised their strategy. As the largest fast-food chain in the world, serving close to 70 million people daily, it’s clear that it generates a lot of data. Moreover, they have leveraged that data in many ways as shown below
Use of digital menus
Digital menus are a common phenomenon these days, but McDonald’s has taken it a notch higher by introducing digital menus that change based on real-time data analysis. The menus vary also based on parameters like weather and time of day. Due to this innovation, they recorded a 3% increase in sales in Canada.
Customer Experience
McDonalds are leveraging the application to make it a win-win situation for them and their clients. Users of their app get various benefits like:
- Exclusive deals on the app.
- Avoiding long queues at the counter and drive-thru
On the other hand, when customers pay through the application, McDonald’s not only got money but also vital customer data that includes metrics like:
- Where and when the client goes to the restaurant
- The frequency of their visits
- Preference between a drive-thru or a restaurant
By using this data, McDonald’s can make recommendations and promote deals to increase sales. As a result of this data, they have noticed a more than 30% increase in sales in Japan for clients that used the app.
Autonomous ships, Big Data and AI
Most people know that the future lies in autonomous automobiles, but not many people know that there are also plans to launch autonomous ships. This is due to a collaboration between Google and Rolls-Royce to create autonomous and smart ships. Rolls-Royce will be using the Machine Learning Engine on Google Cloud in its applications to make its vision of smarter and autonomous ships come true.
At first, AI algorithms will be trained using machine learning to identify objects that can be encountered at sea and classify them based on hazard they may pose. The Machine learning algorithms that are currently being used by Google Voice and image search applications. They will also be augmented by massive data sets produced from various devices like sensors, cameras, and cameras on vessels. By combining the cloud-based AI and Big Data application enable data to be shared in real-time to any ship and also to on-shore control centres.
Healthcare, Big Data and AI
One of the issues that many healthcare systems face is matching staffing volumes to patient numbers. At one time you can have very few patients and a huge staff roster. During other times, you have an overflow of patients and a strained workforce. So how do you solve this problem? Embrace AI and Big Data by following the example set by some hospitals in Paris.
Four hospitals in Paris have managed to leverage AI and Big Data to enable nurses, doctors, and hospital administrators to forecast admission and visit rates for two weeks. This enables them to draft in extra staff when they expect high patient volumes leading to reduced wait times and better-quality care.
So how does the system work? Using an open-source AI Analytics platform, the hospitals compiled admission data for the last ten years and external data sets like flu patterns, weather and public holidays. The insights were then used to predict admission rates at different times. Apart from just being used to predict admission rates, such data can be used to reduce wastage and enhance healthcare delivery by forecasting the demand for services.
Big Data, AI and Security
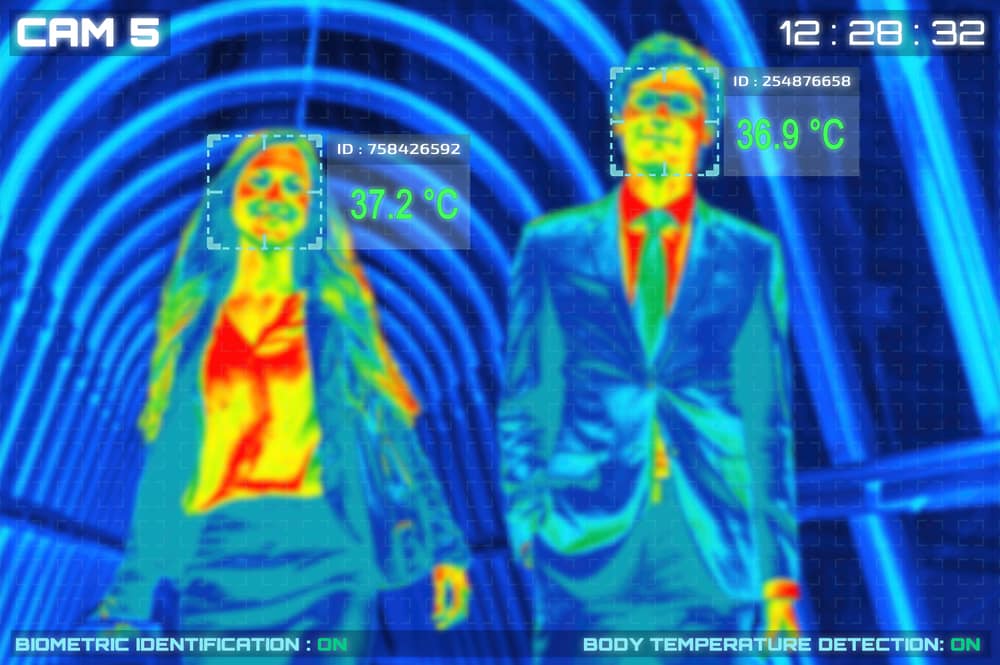
When it comes to security screening, most of us expect that you will find a security person screening you individually using a face-to-face approach. Although customs and immigration officers are highly trained to detect someone that is lying about their intentions mistakes do still happen. Also, there is the fact that humans get tired and can be distracted leading to errors. So how do we avoid such human errors? Apply AI and Big Data to screen passengers.
Homeland security has developed a new system called AVATAR that screens people’s facial expressions and body gestures and picks up small variations that may raise suspicion. The system has a screen with a virtual face that asks the passenger questions. It monitors the person’s responses for changes in voice tone as well as differences in what was said. Data collected is compared to a database and compared against factors that show someone might be lying. If the passenger is flagged as being suspicious then they are highlighted for further inspection.
AI and big data are indeed the fourth revolutions. The potential for AI and Big Data is endless. No industry has been disrupted by AI and Big data, and the future belongs to those that leverage it to their benefit.