Do you know Artificial Intelligence is a combination of several programs and technologies, such as Machine Learning and large language models? All these enable AI to perform tasks autonomously without human intervention.
The advancement and growing interest in AI agents and traditional AI technologies emphasize their key role in work efficiency, resource management, and productivity across various industries.
While AI agents and traditional AI both harness human-like intelligence, they vastly differ in their features and use cases.
This article will give you a detailed comparative analysis of AI agents vs Traditional AI, as both have specific approaches to autonomy and decision-making.
Overview of Traditional AI
Traditional AI, also known as rule-based or standard AI, is an earlier generation of AI systems that uses pre-set algorithms and a set of rules to execute particular tasks. These systems are generally used in a structured environment where users provide specific instructions. Thus, they have limited adaptability and problem-solving skills.
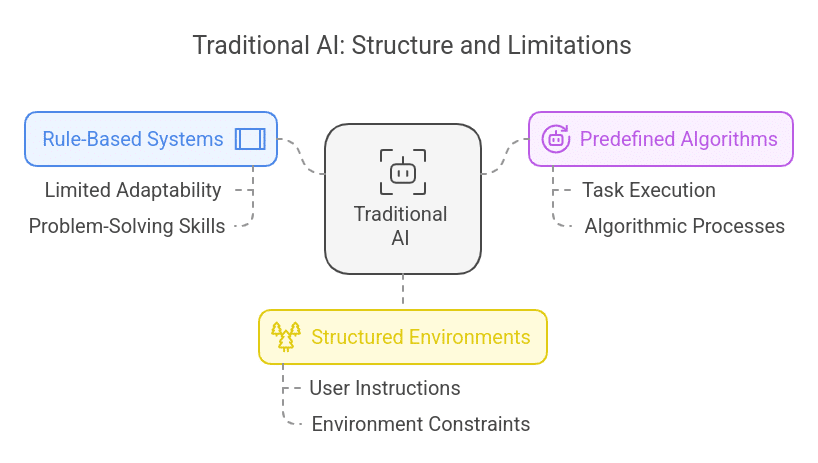
To understand the core functionality of Traditional AI, consider the example of traditional chatbots, which only act on certain inputs. They give users specific options; if users choose from these options, they execute the next task; otherwise, they repeat the options.
While these Traditional AIs perform tasks, they do not learn or enhance their capabilities over time. They can only work and solve problems within their pre-established framework. They struggle to adapt to different data and cases for which the system has not been trained. They only perform tasks that they are programmed for and nothing more.
Introduction to AI Agents
AI agents are the latest-generation or upgraded version of traditional AI that collects data by perceiving its environment and executes suitable actions autonomously by learning or acquiring information to achieve their purpose.
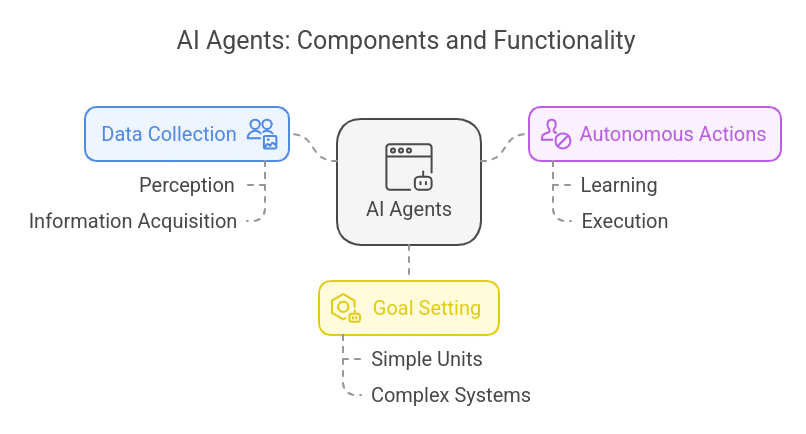
They are classified as autonomous software programs, and their performance is enhanced over time. Users only need to set a goal, and AI chooses the best course of action to achieve it. An AI agent can be a simple unit or a complex system that performs several actions at once.
The most popular examples of AI agents are AI assistants like Alexa, Gemini, Siri, and more. They are designed to interact with humans and learn new information or skills to provide a more immersive user experience. When a user asks a question, these agents look for the best response in their database to answer users' queries. Based on the user input, they can also learn new skills and determine if they can resolve the query.
Besides this, AI agents are being used in development of technologies like big data analytics, machine learning-based model development, and predictive analytics.
Free AI Agents Course: Learn to Build and Use AI Agents
Learn how to build, train, and deploy AI agents for free! Explore hands-on techniques and tools to create intelligent, autonomous systems.
Read in Detail: What are AI Agents?
AI Agents vs. Traditional AI: Comparative Analysis
There are many factors on which you can easily execute a comparative analysis of AI agents and Traditional AI. Here, we will learn the key differences between them based on factors such as autonomy, learning capability, and adaptability.
Autonomy
Certainly, the level of autonomy—the ability to operate freely, decision-making capabilities, and task-performing skills without human intervention—is a critical factor for the comparative analysis of AI agents and traditional AI.
Autonomy in AI Agents
AI agents have complex algorithms for higher autonomy capabilities than Traditional AI, and they can function freely. They sense the environment to make optimal decisions and perform tasks without consistent user instructions.
Additionally, these AI agents can learn and adapt to better workflows from previous experiences and execute complex tasks independently in real-time. This way, they can enhance their decision-making skills based on their experience and algorithms.
Autonomy in Traditional AI
On the other hand, these AI programs often require human intervention or oversight for decision-making and operations. They operate primarily under user direction and follow a set of algorithms or instructions to perform tasks.
Furthermore, these types of AI are made to ease common and recurring tasks like responding to specific keywords, task scheduling, and managing everyday data. They do not function freely and have limited autonomy, relying on user input and predefined rules for decision-making and operations.
Learning Capabilities
Based on their learning capabilities, you can easily compare AI agents and traditional AI to determine which is more suitable for dynamic environments.
Learning Capabilities of AI Agents
In contrast to traditional AI, these AI systems can learn and grow continuously from their environment as they use progressive machine learning codes to adapt to new strategies based on new information.
With this, they handle various problems and can operate new scenarios effectively. Thus, they are more suitable for dynamic environments where changes occur frequently, and adaptation is crucial.
Learning Capabilities of Traditional AI
Generally, you will find limited learning capabilities in Traditional AI as they follow fixed explicit sets of rules and preprogrammed commands that do not change without human intervention. So, to improve this type of AI, you must add new commands and instructions.
Adaptability
Adaptability is another important factor that helps in comparative analysis and understanding of AI Agents and Traditional AI.
Adaptability in AI Agents
These AI agents are highly adaptable and actively interact with the environment to learn and adjust their actions for dynamic changes. Additionally, these AI agents are developed to learn and improve over time from previous experiences to better adapt to their environments. Thus, they can skillfully adapt to new strategies based on current data, making them more resilient to dynamic changes.
Adaptability in Traditional AI
As mentioned earlier, these AIs follow fixed explicit sets of rules and instructions that do not change without human intervention, making them passive in nature with poor adaptability. However, they are more reliable, as they have consistent performance and provide optimal solutions for problems within their framework.
Their performance degrades when the problem falls outside their framework or when the environment changes because they don’t interact with the environment and do not change their behaviour based on responses.
Suggested Read: AI Agents and Agentic AI - Difference and Applications
AI Agents vs. Traditional AI: Use Cases
Use Cases for Traditional AI
Traditional AI has many uses in various industries and day-to-day technologies that demand high precision and reliability. It also excels in other areas such as:
1. Credit Score Checking
Traditional AI uses sort algorithms to review a person’s credentials, including financial details, and allocate them a credit score for their financial services. This automates the manual process, improving work efficiency.
2. Spam Email Filters
The use of AI to determine spam email messages is one of the most common and popular use cases in daily life. These traditional AI systems work on predefined rules to filter spam from incoming emails.
3. Healthcare Devices
In the healthcare sector, traditional AI is used for detailed medical report generation and effective disease diagnosis.
4. E-Commerce Platforms
They help analyze customer behavior to tailor shopping experiences on online shops or websites. They can predict future sales and product demand based on previous sales data, aiding inventory management and optimizing production plans, marketing campaigns, and sales workflows.
5. Logistics and Supply Chains
AI has been used to streamline supply chains and optimize delivery routes. Traditional systems run various operations to find the best delivery route, optimizing overall time and work efficiency.
Use Cases for AI Agents
AI agents possess vast data processing skills and quick decision-making capabilities, making their use versatile in multiple industries. Here are a few use cases of AI agents across various sectors:
1. AI Agents in Web Design
AI can help developers create appealing sites more efficiently and precisely. A web design agency uses AI agents to improve layout design and automate tasks such as choosing colors and fonts based on website niche, target audience, and visitor preferences.
They can also understand customer needs, identify areas for improvement, and optimize content for SEO.
2. AI Agents in the Finance Sector
AI agents enhance security by preventing fraud and data leaks, improving customer service, identifying potential market risks, and managing investments. They analyze transaction patterns and flag suspicious activities.
Additionally, AI-powered agents provide 24/7 customer service, respond to queries, and offer solutions and guidance throughout the financial journey.
3. AI Agents in Healthcare
AI agents revolutionize the healthcare sector by aiding in better patient care, streamlining management tasks, and advancing medical research. They can analyze test results and image data to help medics find diseases easily. Moreover, AI agents can identify potential drugs for new vaccines and optimize drug test patterns.
4. AI Agents in the E-Commerce Sector
Small to large e-commerce platforms use AI agents to improve customer shopping experiences, optimize supply chains, and generate more revenue through Revenue Intelligence.
AI agents interpret customer behaviour, needs, and preferences for better product recommendations, boosting user satisfaction and driving sales. They can also predict product demand to help manage inventory and address overstocking and stockouting issues.
5. AI Agents in Automobile Industries
AI agents power autonomous vehicles, enhance safety, monitor vehicle performance, and predict maintenance needs by analyzing acquired data. Additionally, AI-powered assistants provide drivers with real-time traffic information and route navigation and suggest settings or adjustments based on driver behavior to improve safety.
Also Read: Top AI Tools to Increase Productivity
Conclusion
Now, you know that AI agents may resemble traditional AI, but their functionality differs greatly. AI agents have more autonomy and adaptability and can continuously learn by interacting with their environment.
While traditional AI is more cost-effective and can handle specific tasks with more precision, AI agents provide greater flexibility and efficiency, making them more suitable for complex operations and dynamic environments. AI agents will continue to advance, and their role in making human life more comfortable will only grow.
Related Courses: